 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsFollowing four types of species were observed in a community:
A. Species A has a large effect on community because of its abundance.
B. Species B has a large role in community out of proportion to its abundance.
C. Status of species C provides information on the overall health of an ecosystem.
D. Significant conservation resources are allocated to species D which is single, large and instantly recognizable.
According to above description, species A, B, C, and D are called respectively,
Dominant, Keystone, Indicator and Flagship
Keystone, Flagship, Dominant and Indicator.
Keystone, Dominant, Indicator and Flagship.
Flagship, Dominant, Keystone and Indicator
The diagram represents the competition between species 1 and species 2 according to Lotka-Volterra model of competition.
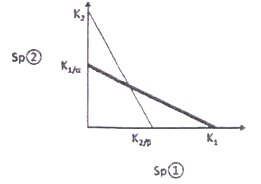
Given the conditions in the diagram, the predicted outcome of competition is
Unstable coexistence between species 1 and 2 because K1 > K2/β and K2 > K1/α.
Unstable coexistence between species 1 and 2 because K1 < K2/β and K2 < K1/α.
Stable coexistence between species 1 and 2 because K1 > K2/β and K2 > K1/α.
Stable coexistence between species 1 and 2 because K1 < K2/β and K2 < K1/α.
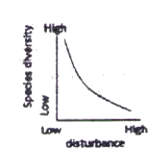
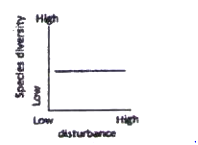
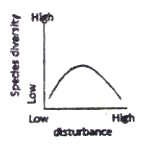
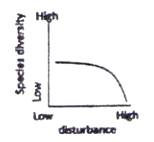
The possible relationships between level of disturbance and species diversity in a biological community are that species diversity.
A. is unaffected by disturbance.
B. is highest at intermediate levels of disturbance.
C. decreases exponentially with increasing levels of disturbance.
D. starts decreasing only at higher levels of disturbance.
An example of the species interaction called commensalism is
nitrogen-fixing bacteria in association with legume plant roots.
microbes in living human gut.
female mosquito deriving nourishment from human blood.
orchid plant growing on the truck of a mango tree.
What parameter, plotted on Y-axis against generation time, would yield the curve shown in the figure?
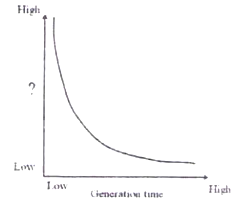
Survivorship
Body size
Lifespan
Intrinsic rate of increase
In which ecosystem is the detrital pathway of energy flow most important?
Lakes
Grasslands
Tropical rain forests
Oceans
Individuals with greater mass have a smaller surface area to volume ratio, which helps to conserve heat. This is known as
Leibig's rule
Cope's rule
Gloger's rule
Bergmann's rule
The dynamics of any subpopulation within a metapopulation differs from that of a normal population in that the
birth rates are lower than the death rates.
death rates are lower than the birth rates.
immigration and emigration rates are significantly higher.
immigration and emigration rates are negligible.
C.
immigration and emigration rates are significantly higher.
The dynamics of a subpopulation within a metapopulation differs from that of a normal population in that the immigration and emigration rates are significantly higher.
The general relation between generation time (T) and population growth rate (r) is described by the equation
lnr = lna - b ln T
r = a - b T
lnr = lna + b ln T
r = a + b T
Which of the following is likely to contribute to the stability of an ecosystem?
High number of specialists
Fewer number of functional links
More omnivores
Linear rather than reticulate food webs
