 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn an animal experiment,
(i) Electrical stimulation of an area in the brain (A) increased a function (F) which was prevented by systemic injection of adrenergic antagonistic, prazosin.
(ii) Injection of carbachol (cholinergic agonist) into A also increased function F which was, however, not prevented by systemic injection of adrenergic antagonistic, prazosin.
The results are likely to be due to stimulation of
Nonadrenergic and cholinoceptive neurons
Cholinergic and non-adrenoceptive neurons
Adrenergic terminals in ‘A’
Both neurons and fibres passing through A
D.
Both neurons and fibres passing through A
The results in an experiment are due to stimulation of both neurons and fibres passing through ‘A’.
Which of the following behavioural changes are expected in a rat when its nucleus accumbens is experimentally ablated?
Aggressive behaviour increases
Explaoratory behaviour decreases
Nest-building activity increases
Level of parental care drops
Character similarity that can be misinterpreted as common descent is called
Symplesiomorphy
Synapomorphy
Homology
Homoplasy
Which of the following evolutionary processes played an important role in the evolution of complex immune system?
Reproductive isolation
Adaptive radiation
Neutral evolution
Co-evolution
In some species of new world monkeys, only one female reproduces in a group. One or more younger females have suppressed reproduction and assist the reproductive female. This is an example of
Sexual selection
Group selection
Kin selection
Reciprocal altruism
In bird species where both parents contribute equally to parental care, generally
Males are larger than females
Females are more colorful than males
Females are larger than males
Both sexes are morphologically similar
Identify the characters shown in the diagram depicting phylogentic relationships among major groups of ferns and fern allies.
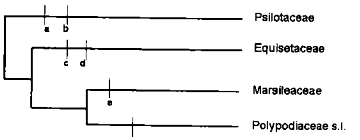
a) Roots absent; b) Sporangiophores; c) Vertical, interrupted annulus; d) Heterospory; e) Leaves scales like, f) Elaters.
a) Roots absent; b) Leaves scale like; c) Sporangiophores; d) Elaters; e) Heterospory; f) Vertical, interrupted annulus
a) Leaves scale like; b) Sporangiophores; c) Elaters; d) Heterospory; e) Roots absent; f) Vertical, interrupted annulus
a) Heterospory; b) Roots absent; c) Elaters; d) Sporangiophores; e) Leaves scale like; f) Vertcal, interrupted annulus.
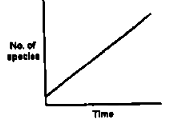
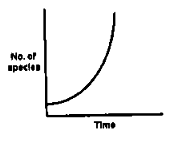
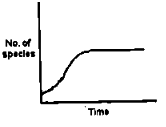
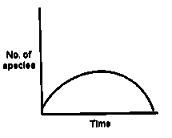
If the number of new species evolving is directly proportional to the number of existing species and the probability of extinction of any species is inversely proportional to the number of existing species, the number of species present at a time during evolution will follow a curve given by:
Some important events in the history of life on Earth are given below:
A. First vertebrates (jawless fishes); first plants.
B. Forest of ferns and confers; amphibians arise; insects radiate
C. Confiers dominant; dinosaurs arise; insects radiate
D. Flowering plants appear; climax of dinosaurs followed by extinction.
E. Radiation of flowering plants, most modern mammalian orders represented.
F. Ice ages, Modern humans appear
Match the above with the geological time periods and choose the correct combination,
A – Silurian; B – Permian; C – Triassic; D – Jurassic; E – Cretaceous; F – Tertiary
A – Ordovician; B- Carboniferous; C – Triassic; D – Cretaceous; E – Tertiary; F – Quaternary
A – Cambrian; B – Ordovician; C – Silurian; D – Devonian; E – Permian; F – Tertiary
A- Devonian; B – Permian; C – Triassic; D – Cretaceous; E – Tertiary; F – Quaternary
