 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe population density of an insect species increases from 40 to 46 in one month. If the birth rate during that period is 0.4, what is the death rate?
0.25
0.15
0.87
0.40
During which geological period was there an explosive increase in the number of many marine invertebrate phyla?
Ordovician
Devonian
Permian
Cambrian
D.
Cambrian
In the Cambrian period there was an explosive increase in the number of many marine invertebrate phyla.
An extraordinary sensory ability that elephants possess is
emission and detection of ultra-high-frequency sounds.
emission and detection of ultra-low-frequency sounds.
detection of changes in the earth's magnetic field.
possession of ultraviolet vision
According to which evolutionary theory, there are long periods without significant evolutionary changes interrupted by short episodes of rapid evolution?
Punctuates equilibrium
Saltation
Mutation
Neutrality
The mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ) of body size in a Drosophila population are 8.5 and 2.2 mm, respectively. Under natural selection over many generations the μ and σ of body size change to 8.5 and 0.8mm, respectively. The type of natural selection responsible for the change is called,
directional
neutral
disruptive
stabilizing
Compared to K-selection, r-selection favours
rapid development, smaller body size and early, semelparous reproduction
rapid development, smaller body size and early, iteroparous reproduction
slow development, larger body size and late, iteroparous reproduction.
slow development, smaller body size and late, iteroparous reproduction
In a population at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the genotype frequencies are: f(A1A1) = 0.59; f(A1A2) = 0.16; f(A2A2) = 0.25. What are the frequencies of the two alleles at this locus?
A1 = 0.59; A2 = 0.41
A1 = 0.75; A2 = 0.25
A1 = 0.67; A2 = 0.33
A1 = 0.55; A2 = 0.44
Brothers A and B have the same father but different mothers. B wants A to help him, which involves both benefits (b) and costs (c) for A. If A incurs a cost of 30 'Darwinian fitness units' in that act, under what condition should be help B, following Hamilton's rule?
only if b > 30
only if b > 60
only if b > 120
only if b > 240
Following is the list of some important events in the history of life and the names of the epochs of Cenozoic era.
Events-
A. Angiosperm dominance increase; continued radiation of most present day mammalian orders.
B. Major radiation of mammals, birds and pollinating insects.
C. Origins of man primate groups.
D. Origin of genus Homo.
E. Appearance of bipedal human ancestors.
F. Continued radiation of mammals and angiosperms, earliest direct human ancestors.
Epochs -
(i) Paleocene; (ii) Pleistocene; (iii) Oligocene; (iv) Pliocene; (v) Eocene; (vi) Miocene
Which one of the following is the correct match of events with the epochs?
A - (v); B - (ii); C - (i); D - (iii); E - (iv); F - (vi)
A - (vi); B - (i); C - (ii); D - (iv); E - (iii); F - (v)
A - (v); B - (i); C - (iii); D - (ii); E - (iv); F - (vi)
A - (iv); B - (i); C - (ii); D - (iii); E - (v); F - (vi)
In the evolutionary tree given below, terms A, B, C, D, and E, represent respectively
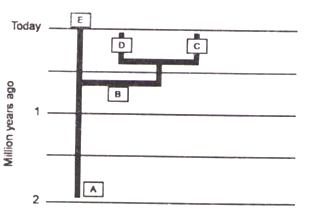
Homo erectus, Homo heidlebergensis, Neanderthal, Denisovan and Homo sapiens.
Homo heidelbergensis, Homo erectus, Denisovan, Neanderthal and Homo sapiens.
Homo erectus, Homo heidelbergensis, Denisovan, Neanderthal and Homo sapiens.
Homo heidelbergensis, Homo sapiens, Denisovan, Neanderthal, and Homo erectus.
