 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe "Red Queen Hypothesis" is related to
the mating order in the harem of a polygamous male.
the elimination by deleterious mutations by sexual reproductions.
mate selection process by a female in a lek.
the evolutionary arms race between the host and the parasite.
Individual A can derive 'fitness' benefit of 160 units by helping Individual B, but incurs a 'fitness' cost of 50 units in doing so. Following Hamilton's Rule, A should help B ONLY if B is his
brother or sister
first cousin only
cousin or uncle
nephew or niece
In several populations, each of size N = 20, if genetic drift results in a change in the relative frequencies of alleles,
A. What is the rate of increase per generation in the proportion of populations in which the allele is lost or fixed?
B. What is the rate of decrease per generation in each allele frequency class between 0 and 1?
The correct answer for A and B is:
A - 0.25; B - 0.125
A - 0.025; B - 0.0125
A - 0.0125; B - 0.025
A - 0.125; B - 0.25
Which of the following statements about evolution is NOT true?
Evolution is the product of natural selection.
Evolution is goal-oriented
Prokaryotes evolve faster than eukaryotes
Evolution need not always lead to a better phenotype.
The origin and diversification of Angiosperms was during which geological period?
Permian
Triassic
Jurassic
Cretaceous
Which one of the following conditions is NOT likely to favour male monogamy?
When the male has to guard his mate against mating by another male.
When the male wants to spend more time for foraging.
When the male has to assist the mate in brood and nestling care.
When the female guards her mate against seeking other females to mate.
A particular behavioural variant affects the fitness of an organism. The relationship between the frequency of the variant in the population and fitness are plotted below. In which of these cases is the behavioural variant likely to reach a frequency of 1?
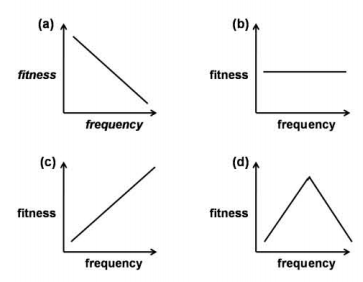
Only b
Only c
b and d
a and d
B.
Only c
In figure c, the behavioural variant is likely to reach a frequency of 1.
Following is a cladogram showing phylogenetic relationships among a group of plants:
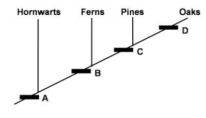
In the above representation, A, B, C, and D respectively represent.
xylem and phloem, embryo, flower, seed
embryo, xylem and phloem, seed, flower
embryo, xylem and phloem, flower, seed
xylem and phloem, flower, embryo, seed
Match major events in the history of life with Earth's geological period.
| Event | Geological period |
| A. First reptiles | i. Quaternary |
| B. First mammals | ii. Tertiary |
| C. First humans | iii. Cretaceous |
| D.First amphibians | iv. Triassic |
| v. Carboniferous | |
| vi. Devonian |
A - v; B - i; C - ii; D - v
A - v; B - iv; C - i; D - vi
A - vi; B - iv; C - ii; D - vi
A - iii; B - i; C - vi; D - v
