 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsBacteriophage T4 infects E. coli and injects its DNA inside the cell. The transcription of viral genes occurs in three stages: immediate-early, early, and late. All the promoters on the viral genome are available, but the control takes place at the level of
promoter strength
modification of host RNA polymerase
synthesis of new polymerases
turn over rate of RNA synthesis
A segment of B-DNA encodes an enzyme of molecular mass 50 kD. The estimated length of this segment in μm would be
0.1547
0.1547 × 10-3
0.4641
0.4641 × 10-3
The diploid genome of a species comprises 6.4 × 109 bp and fits into a nucleus that is 6μm in diameter. If base pairs occur at intervals of 0.34 nm along the DNA helix, what is the total length of DNA in a resting cell?
3.0 m
3.5 m
2.2 m
4.0 m
Phosphorylation of serines as well as methylation and acetylation of lysines in histone tails affect the stability of chromatin structure above the nucleosome level and have important consequences for gene expression. The resulting changes in charge are expected to affect the ability of the tails to interact with DNA because.
DNA is negatively charged.
DNA-histone interaction is independent of net charge.
Phosphorylation of serine increases DNA-histone interaction.
Methylation and acetylation of lysine increases DNA-histone interaction
During the elongation step of protein synthesis, translocation moves the mRNA and the peptidyl t-RNA by one codon through the ribosome. Translocation in E.coli involves GTP and EF-G. However, in vitro translocation can take place independent of GTP and EF-G. Based on these observations, the following hypotheses can be made:
(A) The molecular mechanism of translocation in vitro is completely different from that in vivo.
(B) Translocation activity is independent of GTP hydrolysis.
(C) Translocation activity is completely dependent on GTP and EF-G.
(D) Translocation activity is inherent in ribosomes, however, the rate of translocation in vivo is enhanced significantly in the presence of GTP and EF-G.
Which one of the following combinations is correct?
only (D)
(A) and (C)
(A) and (B)
(C) and (D)
In an experiment on transposition in an eukaryotic system, an intron was cloned within a transosable element and allowed to transpose from a plasmid to genomic DNA. The intron was found to be absent in the transposable element in its new location. It is
not a case of transposition.
a case of replicative mode of transposition.
a case of conservative mode of transposition.
a retrotransposon
Knox genes code transcriptional factors important for the regulation of indeterminate growth in plants shoots. These genes also regulate patterns of development of plant organs such as leaves and flowers. The figure represents a phylogenetic tree of the multigene family in some land plants. The circles represent genes that act to maintain shoot apical meristem (equivalent to stem cells). Orthologues are genes that duplicate due to speciation and paralogues are genes that duplicate within a species.
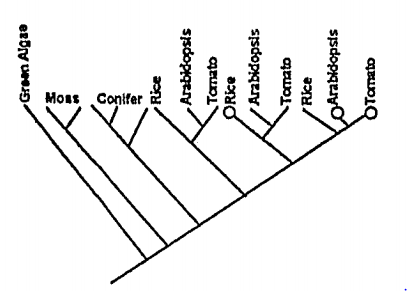
From the figure, the following inferences were made-
(A) Multiple gene duplication occurred in vascular plants.
(B) Gene duplications may have enabled shoot diversification in vascular plants.
(C) Shoot apical meristems are regulated by orthologous genes in vascular plants.
(D) Shoot apical meristems are regulated by paralogous genes in vascular plants.
Which of the following represents a combination of correct inferences?
(A), (B) and (D)
(A), (B) and (C)
(B) and (C) only
(B) and (D) only
In bacteria, chromosomal DNA replication starts at
one specific locus
several specific loci
a single locus, randomly
from several loci, randomly
A.
one specific locus
Replication of the bacterial chromosome is initiated at a single oriC region, i.e. at a specific locus.
The 'Uvr ABC' repair mechanism is involved in repairing
missing bases
strand break
cross linked strands
DNA damage caused by 'bulky' chemical adducts.
Which of the following is NOT a post-translational modification in a mammalian system?
Palmitoylation
Glycosylation
Peptidylation
Phosphorylation
