Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn a plant species, a segregating line (one that contains both homozygotes and heterozygotes at a locus) can be made homozygous by repeated selfing for several generations. What is the level of remaining heterozygosity after three generations of selfing, if the level of heterozygosity in generation'0' is denoted as 1?
0.5
0.25
0.125
0.0625
Given below is the result of a complementation test for six independent mutants(1 to 6).
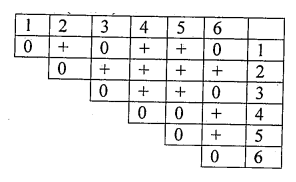
'+' represents complementation; '0' represents non-complementation.
Based on the above, which one of the following conclusions is correct?
The mutations can be ordered in a single cistron as 1-3-5-2-4-6.
All mutations belong to a single cistron, but their order cannot be determined.
There are three cistrons, mutations 1, 3, and 6 represent one cistron, 4 and 5 represent the second cistron and 2 represents the third cistron.
There are three linkage groups, mutations 1, 3 and 6 represent linkage group A, 4, and 5 represent linkage group B, and 6 represents linkage group C.
In a hospital three babies were mixed up. the blood group of the babies were A, B and AB. In order to identify the parents of the babies the blood groups of the parents were determined. the results obtained were:
Parent set 1 - A and AB
Parent set 2 - AB and O
Parent set 3 - B and AB
Which of the following conclusions can be definitively made?
The baby with blood group A is the child of the parent set 2.
The baby with blood group AB is the child of the parent set 1.
The baby with blood group B is the child of the parent set 3.
The parentage of none of the babies can be determined from the given information.
There are two mutant plants. One shows taller phenotype than wild type, whereas the other has the same height as the wild type. When these two mutations were brought in together by genetic crosses, the double mutant displayed even taller phenotype than the tall mutant plants. This genetic interaction is called
antagonistic interaction
additive interaction
synergistic interaction
suppressive interaction

The distribution of heights and weights in a population is shown above in a 2-parameter scatter plot. The size of the square is proportional to the number of persons having a particular combination of weight and height. Which statement best describes the trend in the population?
Height and weight are strongly correlated.
Height and weight are anticorrelated.
Large heights do not imply proportionately large weights.
Height and weight are independent characteristics.
A cross is made between a pure breeding plant having red coloured flowers with a pure breeding plant having white coloured flowers. Such a cross is called as
test cross
monohybrid cross
dihybrid cross
back cross
A cis-trans complementation test is carried out to identify
if two mutations are allelic in nature
if two genes interact with one another
the number of genes influencing a phenotype
to understand the dominance/ recessive relationships between alleles
The following is the inheritance pattern of a trait under observation:
(i) The trait often skips a generation.
(ii) The number of affected males and females is almost equal.
(iii) The trait is often found in pedigree with consanguineous marriages.
The trait is likely to be
autosomal recessive
Autosomal dominant
Sex-linked recessive
Sex-linked dominant
Greater male investment in the care of offspring is most likely to lead to
a lek system
stronger female choice
reverse sexual dimorphism
run-away selection
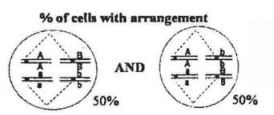
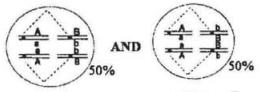
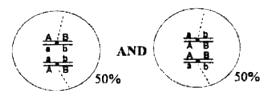
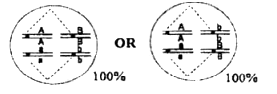
Which of the following representations of chromosomal arrangement in meiotic metaphase I best explains the Law of Independent Assortment?