 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich of the following statements are true for Robertsonian translocations?
A. The size of the homologous chromosome involved in translocation will differ.
B. Genes on the chromosome involved in translocation will show linkage with genes with which it normally independently assorts.
C. There will be a change in the physical map, but no change in the genetic map.
D. It can be identified by G-banding of chromosomes.
E. It can be identified by C-banding of chromosomes.
F. It can lead to Down syndrome.
Which one of the following combinations is correct?
A, C, and D
A, D, and F
A, B, D, and F
A, C, E, and F
The genetic map of three genes in Drosophila melanogaster is given below:
![]()
A cross, as given below is made between individuals of the genotype:
![]()
The female F1 progeny are test crossed and 1000 progeny are obtained. Assuming that there has been no double crossover, what is the expected number of progeny with the genotypes:
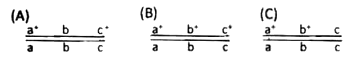
Select the set which shows the correct number of expected progeny.
| Set | (A) | (B) | (C) |
| 1. | 100 | 50 | 850 |
| 2. | 50 | 25 | 425 |
| 3. | 100 | 850 | 50 |
| 4. | 0 | 425 | 75 |
The following pedigree shows the inheritance pattern of a rare disorder with complete penetrance.
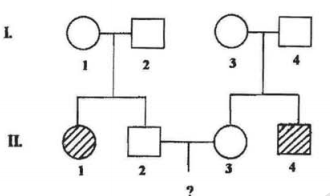
A child from marriage between individuals I 1 - 2 and II 3 will show the disorder only if the parents carry the recessive allele. What is the probability that the child will show the disorder?
1/9, and the probability of the parents to carry the recessive allele is 2/3.
1/4, and the probability of the parents to carry the recessive allele is 3/4.
1/16, and the probability of the parents to carry the recessive allele is 2/3.
1/64, and the probability of the parents to carry the recessive allele is 3/4.
DNA from a strain a bacteria with genotype a+ b+ c+ d+ e+ was isolated and used to transform a strain of bacteria that was a- b- c- d- e-. The transformed cells were tested for the presence of donated genes. The following genes are found to be co-transformed
i. a+ and d+
ii. b+ and e+
iii. c+ and d+
iv. c+ and e+
The order of genes on the bacterial chromosome is
a - b - c - d - e
a - d - c - e - b
a - c - d - e - b
a - d - b - e - c
In the following example, 3 independently assorting genes are known to govern coat color in mice. The genotype of few of the coat colors is given below:
Agouti : A - B - C -
Black : aa B - C -
Albino : -- -- cc
What will be the expected frequency of albinos in the F2 progeny from crosses of pure black with albino of the genotype AAbbcc?
1/4
1/16
1/61
9/64
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bee). On intercrossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio:
9 black : 3 brown : 4 yellow
This is an example of
recessive epistasis where allele e is epistatic to B and b.
dominant epistasis where allele E is epistatic to B and b.
recessive epistasis where allele e is epistatic to E.
complementary epistasis where allele b is epistatic.
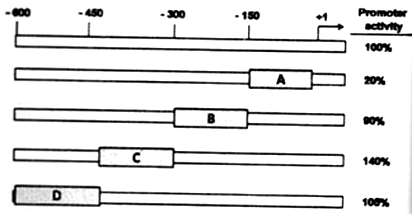
In order to identify the regulatory regions of a novel promoter sequence shown above four 150 bp deletion constructs were made in a luciferase reporter system as indicated above in boxes A to D. After transfection, the observed level of promoter activity (%) as analyzed by luciferase assay of all the constructs is indicated in the right of the figure. Identify the best correct combination of regions in the options given below that indicate the presence of a positive and a negative regulatory element, respectively.
B and D
A and C
A and D
A and B
Assume that in terms of 'genetic fitness' the benefit of performing an altruistic act to a relative is 500 units and the 'cost' involved is 150 units. Following Hamilton's Rule, the act should be performed if the relative is a
only brother
nephew or niece
brother or step-sister
only step-sister
The following table summarizes the result of a cross between two strains of Neurospora having the alleles D and d, respectively. The table shows the different patterns of octad arrangement and the number of ascus observed if each type.
| D | d | D | d | D | d |
| D | d | D | d | D | d |
| D | d | d | D | d | D |
| D | d | d | D | d | D |
| d | D | D | d | d | D |
| d | D | D | d | d | D |
| d | D | d | D | D | d |
| d | D | d | D | D | d |
| 115 | 125 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 13 |
Number of ascus observed = 300
Based on the above, fill in the blanks from the options given below:
"The first two columns are from meiosis with no crossover between locus D and [A]. The patters for these two columns represent [B] segregation pattern. the distance between the locus D and the centromere is [C] map units."
[A] - d allele; [B] - first division; [C] - 10
[A] - centromere; [B] first division; [C] 10
[A] d allele; [B] - second division; [C] - 20
[A] - centromere; [B] - second division; [C] - 10
The inheritance pattern of a common trait which shows complete penetrance is shown below:
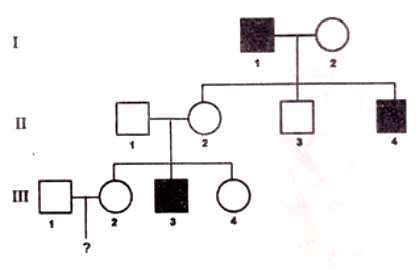
Based on the above pedigree, fill in the blanks from the options given below:
"The trait is [A[. The probability that a child from the marriage of individual III-1 and III-2 will show the trait is [B], considering that the individual III-1 is a carrier of the trait."
[A] - Y-linked; [B] - 0
[A] - Y-linked; [B] - 1/2
[A] - Autosomal; [B] - 1/8
[A] - Autosomal; [B] - 1/6
