 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe following pedigree represents inheritance of a trait in an extended family:
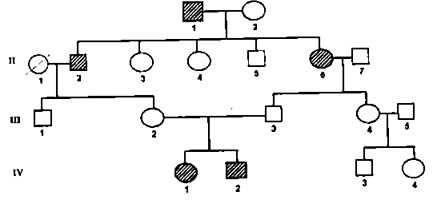
What is the probable mode of inheritance and which individuals conclusively demonstrate this mode of inheritance?
Autosomal recessive, III-2, 3 and IV-1, 2 conclusively demonstrate the mode of inheritance.
Autosomal recessive, I-1, 2 and II-2 conclusively demonstrate the mode of inheritance.
Autosomal dominant, III-2, 3 and IV-1, 2 conclusively demonstrate the mode of inheritance
X-linked recessive, II-3, 4 and 5 conclusively demonstrate the mode of inheritance
Following tree represents phylogenetic relationships among species of a moth family. Circles represent species having eye spots on the wings. Other species do not have eye spots.
IMAGE
The following inferences were made by different researchers:
A. Eye spots were present in the ancestors and some species lost them.
B. Eye spots were not present in the ancestors.
C. Eye spots were lost more than once in evolution of the family.
D. Eye spots were gained only once while evolving from ancestor without them.
Which of the inferences are correct?
A and B
C and D
A and C
B and D
C.
A and C
The inferences that are correct:
Eye spots were present in the ancestors and some species lost them.
Eye spots were lost more than once in evolution of the family.
Twenty small population of a species, each polymorphic for a given locus(T, t) were bred in captivity. In 10 of them the population size was kept constant by random removal of individuals, while other 10 were allowed to increase their population size. After several generations it was observed that in 7 of the size restricted populations only T was present, in the remaining 3 only t was present. In the growing populations 8 retained polymorphism and in 2 only t was observed. The experiment illustrates
Genetic drift which is more likely in large populations.
Genetic drift which is more likely in small populations.
Density dependent selection against T.
Density dependent selection against t.
The Triver-Willard hypothesis states that the physiological state of a female can bias the sex ratio of offspring. In an experiment in the bird species a group of females were fed a diest 30% lower in calories than the control females. After allowing both the groups to mate and breed freely, the offspring of control 1 group were 22 males and18 females. The diet restricted females laid a total of 40 eggs. What should be the minimum deviation from the control to conclude that they have significantly female biased offspring sex ratio. (Chi sq [0.05]df = 1 is 3.84)
18 male 22 female
20 male 20 female
15 male 25 female
10 male 30 female
In a transformation experiment, donor DNA from an E.coli strain with the genotype Z-Y+ was used to transform a strain of genotype Z-Y+. The frequencies of transformed classes were:
Z-Y+ 200
Z-Y 400
Z-Y+ 400
Total 1000
What is the frequency (%) with which Y locus is co-transformed with the Z locus?
1
20
33.3
40
A Tall plant with Red seeds (both dominant traits) was crossed with a dwarf plant with white seeds. If the segregating progeny produced equal number of tall red and dwarf white plants, what would be the genotype of the parents?
TtRr x TtRR
TtRr x ttrr
TTRR x ttrr
TTRR x TtRr
How many genetically different gametes can be made by an individual of genotype AaBbccDDEe, assuming they are independently assorting?
3
5
8
32
Mutation at two different loci of the same gene X results in altered functions. These two mutated version of the gene X are called
Alleles
Complementation group
Interrupted genes
Linkage groups
A gene encoding tRNA undergoes a mutational event n its anticodon region that enables it to recognize a mutant nonsense codon and permit completion of translation. Such a mutation is known as
silent mutation
neutral mutation
reversion
nonsense suppressor
