 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo plants with white flowers are crossed. Whit flowers arise due to recessive mutation. All F1 progeny have red flowers. When the F1 plants are selfed, both red and white-flowered progeny are observed. In what ratio will red-flowered plants and white-flowered plants occur?
1 : 1
3 : 1
9 : 7
15 : 1
The following pedigree shows the inheritance of a common phenotype controlled by an autosomal recessive allele. The probability of carriers in the population is 1/3.
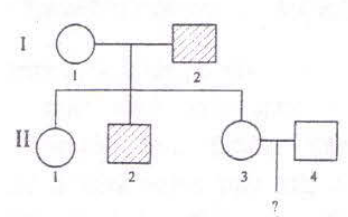
What is the probability that a child from parents II-3 and II_4 will show the phenotype?
1/ 16
1/18
1/36
3/16
B.
1/18
The probability that a child parents II-3 and II-4 will show the phenotype is 1/18.
Genes A, B, and C control three phenotypes which assort independently. A plant with the genotype Aa Bb Cc is selfed. What is the probability for progeny which shows the dominant phenotype for AT LEAST ONE of the phenotypes controlled by genes A, B and C?
1/ 64
27/ 64
63/ 64
Cannot be predicted
In an experiment, clones of a plant is grown in a field. The plants were observed to be of different heights. When a graph was plotted for frequency of plants (Y-axis) against different heights (X-axis), a bell-shaped curve was obtained. From the above it can be concluded that the observed variation in height is due to
it being a polygenic trait.
environmental effect
Variation in genotype
influence of environmental on different genotypes.
The most commonly used molecular tool for phylogenetic analysis involves sequencing of
mitochondrial DNA
mitochondrial RNA
ribosomal RNA
nuclear DNA
A cross was made between Hfr met+ arg+ leu+ strS X F- met- arg- leu- strR, in which leu+ exconjugates are selected. If the linear organization of the genes are leu+ arg+ met+, which one of the following genotypes is expected to occur in the lowest frequency?
leu+ arg- met-
leu+ arg+ met-
leu+ arg+ met+
leu+ arg- met+
Two homozygous individuals (P1 and P2) were genotyped using dominant DNA markers A and B, as shown below. The F1 progeny obtained was test crossed. The frequency of progeny with which different genotypes appear, is given below:
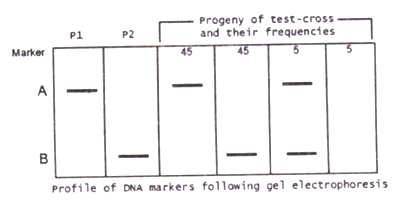
The following conclusions were made:
A. In the F1, markers A and B are linked and in coupling phase (cis).
B. In the F1, markers A and B are linked and in repulsion phase (trans).
C. The distance between A and B is 10 cM.
D. The distance between A and B is 5 cM.
Which of the above conclusions are correct?
A and C
A and D
B and C
B and D
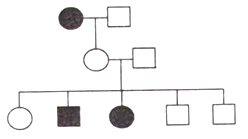
The above pedigree sows the inheritance of a rare allele. The allele is
X-linked recessive
Autosomal recessive
Dominant with incomplete penetrance
Autosomal recessive with incomplete penetrance
Somatic recombination was caused by mild exposure to radiation on flies heterozygous for a given allele during specific stages of development and the individuals were allowed to develop. Such individuals are likely to have
A. clones of homozygous cells in heterozygous body.
B. site specific mutagenesis.
C. twin spots, i.e. patches of mutants cells and homozygous wild type cells in heterozygous body.
D. tissue specific expression of the given allele.
Which of the following combination of answers will be most appropriate?
A and B
B and C
A and c
C and D
Sickle cell anemia is a recessive genetic disease caused due to a point mutation in the 6th codon abolishing one of the MspII endonuclease digestion site present in the β-globin gene. MspII digested DNA from a normal person gives two bands, 1150 bp and 200 bo, in β-globin gene. A family with a proband (based on the disease phenotype) gave the following MspII digestion pattern:
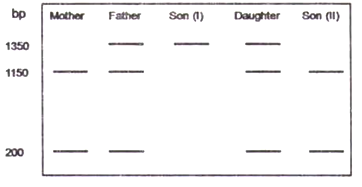
The following conclusions were draw:
A. Son (I) is the proband and the given mutation is not present in Son (II).
B. The daughter is a carrier for the given mutation.
C. The gene is X-linked and thus are affected.
D. A de Novo mutation in same site on normal allele has allowed appearance of disease phenotype in the proband.
Which of the following combination of conclusions will be the most appropriate for the figure given above?
A,B and E
A, B and C
B, C and E
C and D
