 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn Burkitt's Lymphoma a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 8 and 14 is observed. If an individual is heterozygous for this translocation, the consequence in meiosis will be as follows:
A. Four chromosomes, i.e. normal chromosome 8 and 14, and translocated chromosome 8 and 14, pair together.
b. The two normal chromosomes 8 and 14 and two translocated chromosomes pair separately.
C. All gametes produced from this meiosis are non-viable as they have deletions and duplications.
D. In one of the cross configurations called "alternate segregation" all gametes having normal or translocated chromosomes, survive.
E. The gametes having normal chromosomes only survive while all gametes having translocated chromosomes are non-viable, hence the translocations are non-viable, hence the translocations are used as crossover suppressors.
Which of the following combinations best describes the meiotic consequences for the translocation described above?
B and E
B, C, and E
A, C, and E
A and D
The inheritance of a given disorder is recorded in three small families shown below:
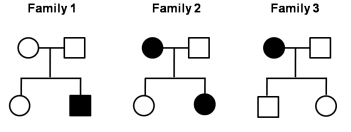
Based on the above-limited information, which one of the following inheritance pattern best explains the observations?
X-linked recessive
X-linked dominant
Autosomal recessive
Autosomal dominant
The following table shows mapping data from three interrupted mating experiments using three different Hfr strains and an F- strain:
Appearance of genes in F-cells:
| Hfr 1 | Genes | e+ | f+ | c+ | d+ | b+ |
| Time | 6 | 24 | 34 | 49 | 54 | |
| Hfr 2 | Genes | b+ | d+ | c+ | f+ | g+ |
| Time | 1 | 6 | 21 | 31 | 63 | |
| Hfr 3 | Genes | d+ | c+ | f+ | e+ | g+ |
| Time | 4 | 19 | 29 | 47 | 61 |
(Time is represented in minutes)
The following answers are derived:
The order of genes is
A. e g b d c f
B. f g b d c e
The distance between
C. f and g is 32 min and between f and b is 30 min.
D. c and e is 28 min and between b and c is 20 min.
The correct combination of answers is
A, C, and D
B and C
A and B
B and D
Two mutant plants, both bearing white flowers, were crosses. All F1 plants had red coloured flowers. When an F1 plant was selfed it produced progeny with either red or white coloured flowers in 9 : 7 ratio. Based on this information, which one of the following conclusions is correct?
The mutations in the parents do not complement each other.
The mutations in the parents are allelic.
The mutations in the parents are non-allelic.
The mutations in the parents are linked.
In a linkage map, two genes A and B, are 70 cM apart. If individuals heterozygous for both the genes are test crossed number of progeny with parental phenotype will be:
equal to the number of progeny with recombinant phenotype.
more than the number of progeny with recombinant phenotype.
less than the number of progeny with recombinant phenotype.
could be more or less than the number of progeny with recombinant phenotype depending on whether the genes are linked in cis or trans, respectively.
A.
equal to the number of progeny with recombinant phenotype.
If individuals heterozygous for both the genes are test crossed number of progeny with parental phenotype will be equal to the number of progeny with recombinant phenotype.
Phages are collected from an infected E. coli donor strain of genotype cys+ leu+ thr+ and used to transduce a recipient of genotype cys- leu- thr-. The treated recipient population is plated on a minimal medium supplemented with leucine and threonine. Many colonies grew. Which one of the following combination of genotypes are appropriate for the colonies that grew?
cys+ leu+ thr+, cys+ leu- thr+, cys- leu+ thr-
cys- leu+ thr+, cys+ leu- thr-, cys+ leu+ thr-
cys- leu- thr-, cys- leu- thr+, cys- leu+ thr-
cys+ leu- thr-, cys+ leu- thr+, cys+ leu+ thr-
Which one of the following statements is NOT TRUE about homologous characters?
Similar traits may not be homologous
Similar traits may be result of convergent evolution
A homologous trait that is derived and shared from a common ancestor is called an autapomorphy.
Homologous characters may show structural similarity but functional diversity.
A male snail homozygous for dextral alleles is crossed with a female homozygous for sinistral alleles. All the F1 individuals showed sinistral phenotype. When F1 progeny snails were self fertilized all individuals of F2 progeny had dextral coiling. This experiment demonstrated
dominant epistasis as dextral allele is dominant over sinistral allele
recessive epistasis as in F2 dextral allele appeared in homozygous condition
maternal effect as the nuclear genotype of the F1 mother has governed the phenotype of the F2 individuals
Scientists discovered two new plant species, “A” and “B” that look similar except that, species “A” bears flowers and leaves that are twice the size of those in species “B”. Which method should the scientists use to appropriately investigate if species “A” is a result of gene duplication in species “B”?
Sequence similarity, gene structure and gene size
Plant size, physical proximity of gene and genome size.
Sequence similarity, physical proximity of gene, genome size
Sequence length, gene structure and chromosome count.
