 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsFollowing is the picture of an inversion heterozygote undergoing a single crossing-over events.
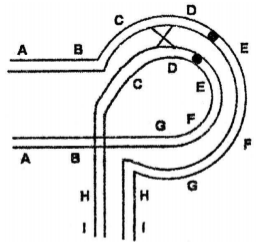
The folllowing statements are giving towards explaining the consequences at the end of meiosis:
(a) The resultants two chromosomes will have deletion and duplications.
(b) A dicentric and an ancentric chromosomes will be formed.
(c) The inversion does not allow crossing over to occur, so even if a crossing over is initiated , it will fail to occur.
(d) The crossing over is considered suppressed by inversion as the acentric chromosomes will not segregate normally.
(e) All the gametes formed wilh cross-over chromatids at the ends of meiosis will be non-viable as they carry large deletion or duplication.
(f) The gametes having non-cross-over (parental) chromatid will survive.
Which combination of statements is correct?
(b) and (e)
(a) and (c)
(b), (d) and (f)
(a), (e) and (f)
D.
(a), (e) and (f)
Option (d) is correct answer.
Polymorphic DNA sequences are used for molecular identification. Short tandem repeats (STRs) and single nucleotide Polymorphism (SNPs) are used as polymorphism markers. The table below summarize the status of autosomal SNP, autosomal STR, mitochondrial SNP, Y-linked STR for four individuals related to each others, representing parents and thier two children.
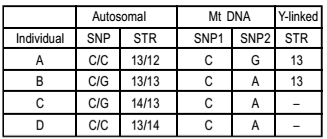
Based on the above data, identify the individuals representing the two parents.
Individuals A and D
Individuals A and C
Individuals B and C
Individuals C and D
An autosomal recessive condition affects 1 newborns in 10,000 in a random mating population without any disruption acting forces. What is the approximate expected frequency of carries in this population?
1 in 1000 newborn
1 in 50 newborn
1 in 100 newborn
1 in 50 newborn
Angelman syndrome (AS) and Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) have very distinct symptoms. Factors responsible for the occurrence of these syndrome are given below:
(A) Microdeletion of 15q11-13 in paternal chromosome.
(B) Uniparental disomy of maternal chromosome 15.
(C) lack of functional maternal copy of ubiquitin ligase E3A.
(D) Lack of SNURF-SNRPN transcript, which is produced only from paternal chrosomoe.
(E) Deficiences of small nuclelor RNAs, which are encoded from the introns of SNURF-SNRPN transcript from paternal chromosome.
Which of the following combination of answers is correct for Angelman and Prader-Willi Syndrome?
PWS-A, C, D: AS-B, E
PWS- B only: AS-A, C, D, E
PWS- A, B, D, E: AS- C only
PWS- A, B : AS- C, D, E
The pedigree below represents the inheritance of an autosomal recessive trait.
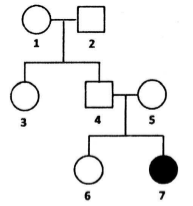
What is the probability that individual '6' is heterozygote?
1/4
1/2
2/3
1/3
The allel l in Drosophila is recessive, sexlinked and lethal when homozygous or hemizygous. If a female of the genotype Ll is crossed with a male, what is the ratio of females: males in the progeny?
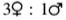
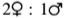
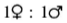
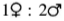
Deamination of bases is a common chemical event that produces spontaneous mutation. Which one of the following bases will be formed by deamination of 5-methylcytosine?
Uracil
Thymine
Cytosine
Guanine
In a population of 2000 individuals of a plant species, genetic difference at a single locus leads to different flowers colours. The alleles are incompletely dominant. The population has 100 individuals with the genotype rr ( white flowers), 800 individuals with the genotype Rr (pink flowers) and the remaining have genotype RR( red flowers). What is the frequency of the r allele in the population?
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
