 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsMeasurement and mapping with spatial resolution the membrane potential of a cell, which is too small for microelectrode impalement, is done using
Radioisotope
Voltage-sensitive dye
pH sensitive chemical
Vital dyes
One of the methods for finding common regulatory motifs present in a set of co-regulated genes is
Prosite
MEME
Mat Inspector
PSSM
In an in-vitro experiment using radiolabelled nucleotides, a researcher is trying to analyze the possible products of DNA replication, by resolving the products using urea-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In one experimental set up RNase H was added (Set 1), while in another set no RNase H was added (Set 2).
The possible observation of this experiment could be
A. There is no difference in the mobility of labeled DNA fragments between the Set 1 and Set
B. There is distinct difference in the mobility of the newly synthesized labeled fragments between Set 1 and Set 2.
C.The mobility of the newly synthesized labelled DNA fragments in case of Set 1 as faster as compared to the Set 2.
D.The mobility of the newly synthesized labeled DNA fragments in case of Set 1 is slower as compared to the Set 2.
Which of the following combinations represent correct observations?
A and B
B and C
A and D
B and D
Bacteriophage λ has two modes in its life cycle, lytic and lysogenic. In the lysogenic mode, the expression of all the phage genes are repressed while the expression gene switches between on an off position depending on the concentration of repressor.
The following statements are made:
A. Repressor may act both as a positive regulator and a negative regulator.
B. Expression of repressor gene, cI is independent of the expression of cII and cIII genes.
C. Mutation of cI gene will cause it to form, clear plaques on both wild type coli and E.coli (λ+).
D. Mutation at operators, OLandORwill allow the phage to act as a virulent phage.
The correct statements are-
A and B
B and C
C and D
D and A
Survival of intracellular pathogens depends on the levels of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in macrophages. In an experimental condition, Mycobacteria infected macrophages were treated with IL-6 or IL-12 for 4 hours at 37°C. Untreated cells were used as control. Cells were lysed and number of bacteria in each experimental set was counted by measuring colony forming unit (CFU). Which of the following observations is true?
IL-12 treated cells contain more intracellular bacteria than control
IL-12 treated contain less intracellular bacteria than control
IL-6 treated cells contain more intracellular bacteria than control
IL-6 treated cells contain less intracellular bacteria than control
The bacterial flagellar motor is a multi-protein complex. Rotation of the flagellum requires movement of protons across the membrane facilitated by a multi-protein complex. The flagellar motor proteins combine to create a proton channel that drives mechanical rotation. In a screen for mutants, some non-motile ones were selected. These could have
Mutations in tubulin and actin proteins
Mutation in kinesin proteins
Mutated H+-ATPase
Mutation in the charged residues lining the ridgeof the FliG subunit
A bacterial response regulator turns on gene A in its phosphorylated form. The amount of ‘A’ shows a sharp and steep rise at a threshold concentration of the signal sensed by the cognate sensor. This is most likely due to
Increased phosphatase activity of the sensor at the threshold concentration
Decreases phosphorylation of the response regulator by the sensor
Cooperativity in binding of the response regulator to the target gene A
Negative feedback in gene A expression
You are given a group of four mice. Each mouse is immunized with keyhole limpet hemocyanin or azobenzene arsonate or lipopolysaccharide or dextran. Four weeks later, sera were collected from these mice and antigen-specific IgG1 and IgG2a ELISA were observed. Only one of the mice showed positive response. It was
Keyhole limper hemocyanin-primed mouse
Azobenze arsonate-primed mouse
Lipopolysaccharide-primed mouse
Dextran-primed mouse
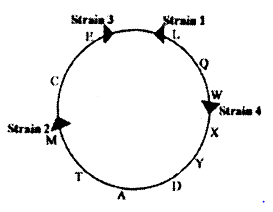
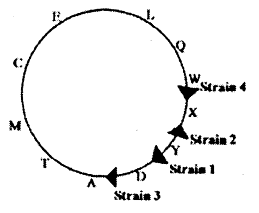
In E. coli four HFr strains donate the following genetic markers in the order shown below:
Strain 1: L Q W X Y
Strain 2: M T A D Y
Strain 3: E C M T A
Strain 4: W Q L E C
Which of the following depicts the correct order of the markers and the site of integration ( ) of the F-factor in the four HFr strains?
![]()
![]()
The following is a schematic representation of region (showing six bands) of the polytene chromosome of Drosophilia, along with the extent of five deletions (Del1 to Del5):
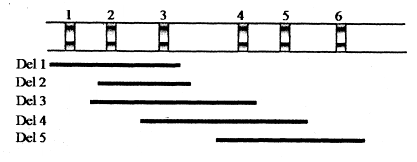
Recessive alleles a, b, c, d, e and f are known to correspond to each of the bands (1 to 6), but their order is not known. When the recessive alleles are placed against each of these deletions, the following results are obtained. The plus (+) in the table indicates wild type phenotype of the corresponding allele, while a minus (-) indicates the phenotype governed by the corresponding mutant allele.
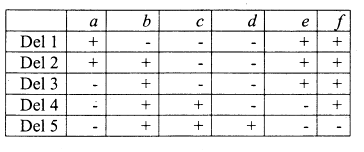
Which one of the following indicates the correct location of the recessive alleles on the bands of the polytene chromosomes?
a - 3; b – 1; c – 2; d – 4; e – 5; f – 6
a - 2; b – 1; c – 3; d – 4; e – 5; f – 6
a - 4; b – 1; c – 2; d – 3; e – 5; f – 6
a - 6; b – 2; c – 3; d – 4; e – 1; f – 5
