 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsPlasmid copy number achieved by plasmid encoded control elements that regulate the initiation of the replication step. For example in stringent plasmid protein Rep A dimerize and binds to origin of replication and do not allow replication more than once. What mutation may convert this stringent mode of replication in plasmid into relaxed one?
Over expression in rep A protein
Mutation in rep A gene in dimerization domain
Mutation in rep A gene in dimerization domain
Gain of function in recognition domain of rep A
What would be the effect on serum concentration of TSH if a bolus of thyroxine is injected to a person?
Remain unchanged
First increase and then come to normal
Initially decrease but after short time will be normal
Remain high for prolonged period of time
Treatment of acetosyringone is given during transfer of transgene using Agrobacterium as vector. The rationale behind this is that acetosyringine
Helps in anchorage of bacteria to plant cell wall
Activates vir operon of bacteria
Helps in intergration of T-DNA in plant genome
Promotes bacterial growth by activating genes in plant
ELISA assays uses
An enzyme which can react with secondary antibody
An enzyme which can react with the antigen
A substrate which gets converted into a coloured product
A radiolabelled secondary antibody
Eukaryotic genomes are organized into chromosomes and can be visualized at mitosis by staining with specific dyes. Heat denaturation followed by staining with Giemsa produced alternate dark and light bands. The dark bands obtained by this process are mainly
AT rich and gene rich regions
AT rich and gene desert regions
GC rich and gene rich regions
GC rich and gene desert regions
A researcher has isolated a restriction endonuclease that cleaves at only one specific 10 base pair site.
A. Would this enzyme be useful in protecting cells from viral infections, giving that a typical viral genome is 5 X 104 base pairs long.
B. Restriction endonucleases are slow enzymes with turnover number of 1 s‐1. Suppose the isolated endonuclease was faster with turnover numbers similar to those for carbonic anhydrase (106s‐1), would this increased rate be beneficial to host cells, assuming that the fast enzymes have similar levels of specificity?
The correct combination of answer is:
(A) : No (B) : Yes
(A) : No (B) : No
(A) : Yes (B) : No
(A) : Yes (B) : Yes
Lac repressor inhibits expression of genes in lac‐operon whereas purine biosynthesis is repressed by the pur repressor. The two proteins have 312% identical sequences and have similar three dimensional structures. The gene regulatory properties of these proteins differ in relation to
A. Binding of small molecules to the repressor
B. Presence of recognition sites on the genome
C. Oligomeric nature of the repressor
D. DNA binding property
The correct statements are
A and B
A, B, and C
A and C
B,C and D
An experiment was designed to find out the relation between DNA uptake and transformation efficiency. 32P‐labelled genomic DNA from Bacillus subtilis (A) and cold genomic DNA from Clostridium jejeuni (B) mixed in various proportions was used to transform Bacillus substilis. The results obtained are tabulated below
| Set no | Concentration of DNA used(µg/ml) A | Concentration of DNA used(µg/ml) B | Uptake of 32Pmlabeled DNA (%) | Transforming efficiency (CFU) |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 90 | 30 |
| 2 | 1 | 10 | 82 | 10 |
| 3 | 1 | 100 | 15 | 5 |
| 4 | 1 | 1000 | 5 | 1 |
The following interpretations (A to D) could be made
A. The transformation is dependent on recombination between homologous sequences.
B. Cells did not distinguish between homologous or heterologous sequences for uptake of DNA.
C. DNA uptake is based on specific receptors.
D. DNA degradation dictates transformation efficiently
Which of the following interpretations are correct?
A and B
A and C
C and D
A and D
Molecular beacons (MB) and Taqman (TQ) are used as probes in Real time PCR experiments. Both these probes are based on the principle of FRET and employ a fluorophore (F) and a quencher (Q). However the mechanism by which they function are different as illustrated below. At what stage of the PCR we would be able to detect fluorescence?
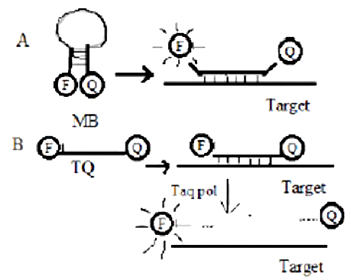
Annealing step for both
Extension step for both
Annealing for A and Extension for B
Extension for A and Annealing for B
C.
Annealing for A and Extension for B
PCR is based on simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: denaturation of the template into single strands; annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
So the PCR is able to detect fluoresecence at the annealing and extension stage.
