 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsBacteriophage λ is a temperate phage. Immediately after infection, viral specific mRNAs for N and Cro proteins are expressed followed by early mRNAs. At the commitment phase, either lytic cycle starts with the expression of genes for head tail, and lytic proteins or lysogenisation cycle begins with the expression of repressor and integrase genes. During induction of lysogens both INT and XIS proteins are needed along with host factors. Out of the four processes below, some govern integration of viral genome and its excision.
A. Repression of transcription
B. Reteroregulation
C. Rearrangement of viral genome
D. Repression of translation
Identify the correct set of combination:
A and B
B and C
C and D
D and A
p24 is an important core protein of HIV. This protein is abundant during active replication of the virus. The serum of an HIV patient was examined for the presence of p24 and antibody against p24 for proper diagnosis of the infection stage. Match the clinical observations in Column A with the inferences in Column B.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. p24 is present in he serum | a. Viral latency |
| B. Anti-p24 antibody is high in the serum | b. Progression of HIV from latency to lytic stage. |
| C. Anti-p24 antibody begins to decline with corresponding increase in p24 | c. Early stage of infection |
Choose the correct matching
A – a; B – b; C – c
A – b; B – a; C – c
A – c; B – a; C – b
A – c; B – b; C – a
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is needed for growth of almost all cells. EGF receptor is a transmembrane protein having an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain and a cytosolic domain of protein tyrosine kinase (PTK). Binding of EGF to the receptor activates PTK resulting in activation of transcription factors through intracellular transducers. In cell type A, much of the extracellular ligand binding domain is deleted by proteases such that cytosolic domain of PTK becomes constitutively active whereas cell type B is having normal EGF receptor. What will be the best-fit graph for the growth of the cultures of cell type A and B in complete medium in presence (+) and absence (-) of EGF?
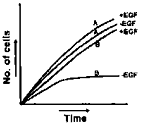
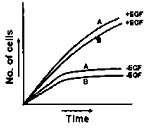
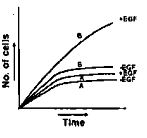
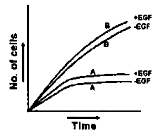
A.

Among the given graphs, the best graph of the cultures of cell type A and B in presence and absence of EGF is graph A.
The RFLP pattern observed for two pure parental lines (P1 and P2) and their F1 progeny is represented below. Further, the P1 plant had red flowers while the P2 had white flowers. The F1 progeny was backcrossed to P2. The result obtained, showing the number of progeny with red and white flowers and their RFLP patterns is also represented below.
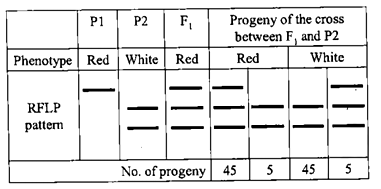
Which one of the following conclusions made is correct?
The DNA marker and the gene for the flower colour are 10 cM apart.
The marker and the gene for the flower are 5cM apart.
The marker and the phenotype are independently assorting.
The marker and the gene for the colour segregate from one another.
Wild type T4 bacteriophage can grow on B and K strains of E. coli forming small plaques. rII mutants of T4 bacteriophage cannot grow on E.coli strain K (non-permissive host), but form large plaques on E. coli B (permissive host). The following two experiments were carried out:
Experiment I : E. coli K cells were simultaneously infected with two rII mutants (a- and b-). Several plaques with wild type morphology were formed.
Experiment II: E. coli B cells were simultaneously infected with the same mutants as above. T4 phages were isolated from the resulting plaques and used to infect E. coli K cells. Few plaques with wild type morphology were formed.
Which one is the correct coclusion made regarding the rII mutants, a- and b- from the above experiments?
The mutations a- and b- belong to two different cistrons (experiment I) and there is no recombination between them (experiment II).
The mutations a- and b- belong to two different cistrons (experiment I) and they recombines (experiment II).
The mutations a- and b- belong to two different cistrons (experiment II) and they recombined (experiment I).
The mutants a- and b- belong to the same cistrons (experiment I) and they did not recombine (experiment II).
An E. coli strain has metB1 (90 min) and leuA5 (2 min) mutations. It also has strA7 (73 min) mutation and Tn5 transposon which confers streptomycin and kanamycin resistance, respectively, inserted in its chromosome. The mutant strain was crossed with an Hfr strain that is streptomycin sensitive in its chromosome. The mutant strain was crossed with an Hfr strain that is streptomycin sensitive and has a hisG2 mutation (44 min) that makes it require histidine. After incubation for 100 min, the cells were plated on minimal plate supplemented with leucine, histidine and streptomycin to select the metB marker. After purifying 100 of the Met+ transconjugants, one finds that 15 are His+, 2 are Leu+ and 12 are kanamycin sensitive. The unselected markers are
A. metb1 and leuA5 mutation
B. leuA5 and Tn5 insertion mutation
Which of the above statement is correct and what is the position of transposon insertion?
A and before 73 min
B and before 44 min
B and before 73 min
A and before 44 min
Locus control region (LCR) lies far upstream from the gene cluster and is required for the appropriate expression of each gene in the cluster. LCR regulates expression of globin genes in the cluster through the following ways:
A. LCR interacts with promoters of individual genes by DNA looping through DNA-binding proteins.
B. The LCR-proteins attract chromatin-remodelling complexes including histone-modifying enzymes and components of the transcription machinery.
C. LCR acts as and enhancer for global regulation of gene cluster and does not regulate individual genes.
D. LCR participates in converting inactive chromatin to active chromatin around the genes cluster.
Choose the correct set of combinations.
A and B
A and C
B and C
B and D
A student wrote following statements regarding comparison of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP), Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD), Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP) and Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs) techniques used for generating molecular markers in plants:
A. All these techniques can be used for fingerprinting.
B. Detection of allelic variation can be achieved only by RFLP and SSRs.
C. Use of radioisotopes is required in RFLP and RAPD only.
D. Polymerase chain reaction is required for all techniques.
Which one of the following combination of above statements is correct?
A and B
B and C
C and D
D and A
In order to clone an eukaryotic gene un pBR322 plasmid vector, the desired DNA fragment was produced by PstI cleavage and incubated with PstI difgested pBR322 (PstI cleavage site lies within the ampicillin resistant gene) and ligated. Mixture of ligated cells were used to transform E. coli and plasmid containing bacteria were selected by their growth in tetracycline containing medium. Which type of plasmids will be found?
Circular pBR322 plasmid containing the target gene and resistant to only tetracycline.
Circular pBR322 plasmid containing the target gene and resistant to tetracycline only and recircularised pBR322 plasmid resistant to both ampicillin and tetracycline.
Circular pBR322 plasmid containing the target gene and resistant to only tetracycline, recircularised pBR322 resistant to both ampicillin and tetracycline and cocatemerized pBR322 resistant to both ampicillin and tetracycline.
Circular pBR322 plasmid containing the target gene and resistant to both ampicillin and tetracycline.
A fluorophore when transformed from solvent A to solvent B results in an increase in the number of vibrational states in the ground state without any change in the mean energies of either the ground or excited state. What would be the change seen in the fluorophore’s emission spectrum?
An increase in emission intensity
An increase in emission bandwidth
An increase in emission wavelength
A decrease in emission wavelength
