 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn a 30-residue peptide, the dihedral angles φ, ψ have been determined by one or more methods. When their values are examined in the Ramachandran plot, it is
not possible for φ, ψ values to be distributed in the helical as well as beta sheet region.
possible that the φ, ψ values are all in the helical region although circular dichroism spectral studies indicate beta sheet conformation.
possible to conclude that the peptide is composed of entirely D-amino acids.
not possible to conclude if the peptide is entirely helical or entirely in beta sheet conformation.
Hydrogen bonds in proteins occur when two electronegative atoms compete for the same hydrogen atom
Donor-H ..... Acceptor
The angle 'θ' between donor and acceptor of a hydrogen bond was determined from large number of X-ray structures of proteins, as shown below:
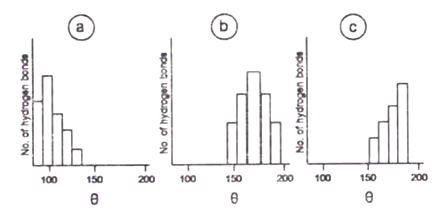
Which one of the distribution of 'θ' was observed from the proteins?
Only b
Onl a
Only c
a and b
In the accompanying figure, reaction kinetics of three proteins (a, b, c) is presented. Protein concentrations used to obtain this data are a - 1 mg/ml; b - 4 mg/ml; c - 2 mg/ml.
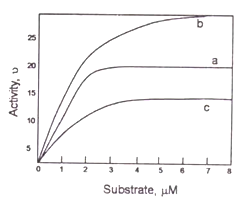
If catalytic efficiency is defined as kcat/Km, which of the following statements is correct?
b > c > a
a > b > c
a > c > b
c > a > b
Lipid rafts are involved in signal transduction in cells. rafts have a composition different from rest of the membrane. Rafts were isolated and found to have cholesterol to sphingolipid ratio of 2 : 1. The estimated size of the raft is 35nm2. If the surface areas of cholesterol is 40 Å2 and sphingolipid is 60 Å2, how many cholesterol and sphingolipids are present in one raft?
50 cholesterol: 25 sphingolipid
200 cholesterol: 100 sphingolipid
40 cholesterol: 20 sphingolipid
20 cholesterol: 10 sphingolipid
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is subject to feed back inhibition by its products in glycolysis. Some of the chemical compounds which might be involved in the process, are listed below:
A. NADH
B. FAD
C. Aceytl-CoA
D. Acetaldehyde
Which one of the following combinations of above chemical compounds is involved in feedback inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
A and B
B and C
C and D
A and C
The fractional clearance of neutral and cationic dextran molecules of various sizes through the kidneys of a rat is shown in the figures below. Which one of the following is correct?
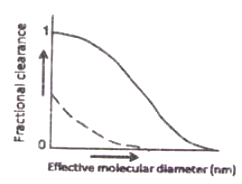
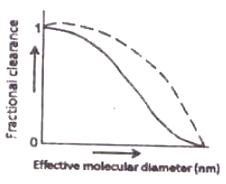
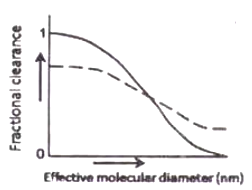
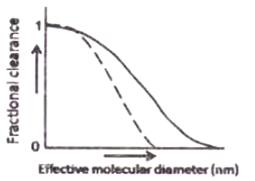
![]()
Which one of the following statements is correct?
Electrospray ionization mass spectrum of a compound can be obtained only if it has a net positive charge at pH 7.4.
Helical content of a tryptophan-containing peptide can be obtained by examining the fluorescence spectrum of tryptophan.
The occurrence of a beta-sheet in a protein can be inferred from its circular dichroism spectrum.
The chemical shift spread for a compound is more in its 1H NMR spectrum as compared to its 13C NMR spectrum.
A mixture of two proteins was subjected to following three chromatographic columns: a) Cation exchange, b) Size exclusion (Sephadex 100) and c) Reverse phase. Following elution profiles were obtained

Which of the following statements is correct?
A is larger and more hydrophobic than B.
B is more anionic and more hydrophobic than A.
A is more hydrophobic and smaller than B.
A is more cationic and smaller than B.
A protein has 4 equally spaced trypsin sensitive sites which results in peptide fragments A1, A2, A3, A4, and A5 upon digestion with trypsin. The peptides A2 and A5 represent N-terminal and C-terminal fragments respectively. Now you are asked to synthesize this protein. At time t = 0 you added all the 20 amino acids labelled with 14C and initiated the synthesis. At time t = 4, full-length protein is synthesized. If you stop the synthesis of the protein in time t = 1 and digest the protein with trypsin, which peptide will have maximum 14C label than others?
A3
A1
A4
A2
Lipid rafts are rich in both sphingolipids and cholesterol. Cholesterol plays a central role in raft formation since lipid rafts apparently do not form in its absence. Why do you think cholesterol is essential for the formation of lipid rafts?
Cholesterol decreases the mobility of sphingolipids in the lipid bilayer.
Large head groups of sphingolipids repel each other in presence of cholesterol.
Cholesterol interacts with fatty acid tails in the membrane.
The planar cholesterol molecules are postulated to fill the voids that form underneath the large head groups of the sphingolipids.
