 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsBoth sphingomyelin and phosphoglycerides are phospholipids. Which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
While one has a fatty acid tail attached via an ester bond, in another, the fatty acid tail is attached via an amide bond.
The hydrophilicity of both is dependent on the phosphate group attached to the phosphate group.
Only one of them may contain a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
Both may have choline as head group.
The turnover number and specific activity of an enzyme (molecular weight 40,000D) in a reaction (Vmax = 4μmol of substrate reacted/ min, enzyme amount = 2μg) are
80,000/ min, 2 × 103 μ mol substrate/ min
80,000/ min, 2 × 103 μ mol substrate/ second
40,000/ min, 1 × 103 μ mol substrate/ min
40,000/ min, 2 × 103 μ mol substrate/ min
Indicate the names of the following molecules
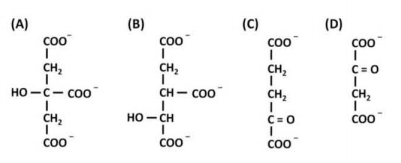
A - isocitrate; B - α-ketoglutarate; C - oxaloacetate; D - citrate
A - citrate; B - isocitrate; C - α-ketoglutarate; D - oxaloacetate
A - isocitrate; B - citrate; C - α-ketoglutarate; D - oxaloacetate
A - citrate; B - isocitrate; C - oxaloacetate; D - α-ketoglutarate
A researcher has developed a program to evaluate the stability of a protein by substituting each amino acid at a time by the other 19 amino acids. For a protein, researcher has observed the following changes in stability upon substitution of amino acids in loops, helices sheets, protein core and on the protein surface.
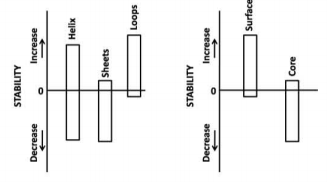
Substitutions in
a. loops are more tolerant
b. sheets are more tolerant.
c. core is less tolerant
d. helices are less tolerant
e. surface is more tolerant
Which of the above statements are correct?
a and c
c and d
b and e
a and b
Indicate which one of the following statements about nucleic acids and proteins structures is correct.
Hydrogen bonding between the bases in the major and minor grooves of DNA is absent.
Both uracil and thymine have a methyl group but at different positions.
The backbone dihedral angles of α-helices and β-sheets are very similar. Only the hydrogen bonding pattern is different.
A β-turn is formed by four amino acids. The type of β-turn is determined by the dihedral angles of the second and third amino acid.
The standard free energy change () per mole for the reaction A B at 30°C in an open system is -1000 cal/ mole. What is the approximate free energy change (G) when the concentration of A and B are 100 micromolar and 100 millimolar, respectively?
3160
316
31610
-3160
A and B are two enantiomeric helical peptides. Their chirality can be determined by recording their
circular dichroism spectrum
UV spectrum
Fluorescence spectrum
Edman sequencing
Which one of the following statements about receptor-enzyme is FALSE?
A receptor-enzyme has an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular catalytic (enzyme) domain.
Many types of receptors enzymes are found in animals.
The signal transduction pathways of receptor-enzyme involve phosphorylation cascades.
Receptor-enzymes interact directly with intracellular G-proteins.
The -COOH group of cellular amino acids can form which of the following bonds inside the cell?
Ether and ester bonds
Ester and amide bonds
Amide and ether bonds
Amide and carboxylic anhydride bonds
Predominant interactions between phospholipids that stabilize a biological membrane include
hydrogen bonds and covalent interactions
van der Waal and ionic interactions
hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding
covalent and hydrophobic interactions.
