 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA protein in 100 mM KCl solution was heated and the observed Tm (midpoint of unfolding) was 60ºC. When the same protein solution in 500 mM KCl was heated, the observed Tm was 65ºC. What is the most probable reason for this increase in Tm?
Hydrophobic interaction is increased and electrostatic repulsion is decreased
Hydrophobic interaction is decreased and electrostatic repulsion is increased
Hydrogen bonding is increased
Van-der Waals interaction is increased
During receptor‐mediated endocytosis, apolipoprotein B on the surface of LDL particle binds to the LDL receptor present in coated pits containing clathrin. The receptor‐LDL complex is internalized by endocytosis, trafficked by lysosome and the LDL‐receptor is finally recycled. A patient reports with familial hypercholesterolemia. This could be due to:
Mutation in the LDL molecule
Defect in LDL receptor recycling
Mutation in the LDL receptor
Defect in cholesterol binding with its receptor
An amino acid contains no ionizable group in its side chain (R). It is titrated from pH 0 to 14. Which of the following ionizable state is not observed during the entire titration in the pH range 0 – 14?
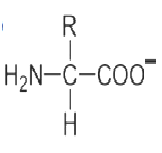
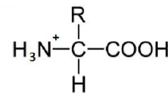
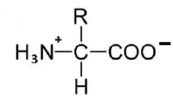
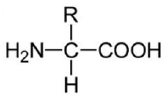
D.


Option (d) is correct.
Amino Acids are weak Polyprotic Acids. They are present as zwitter ions at neutral pH and are amphoteric molecules that can be titrated with both acid and alkali. All of the amino acids have an acidic group (COOH) and a basic group (NH2) attached to the a carbon, and also they contain ionizable groups that act as weak acids or bases, giving off or taking on protons when the pH is altered.
The strong positive charge on the amino group induces a tendency for the carboxylic acid group to lose a proton, so amino acids are considered to be strong acids. Some amino acids have other ionizable groups in their side chains and these can also be titrated.
A 30 residue peptide was treated with trypsin and the peptides were separated by HPLC. Four peaks A B, C and D were obtained. Peptides corresponding to A, B, C and D were reduced and alkylated selectively at cysteine residues. The sequence obtained from A. B, C and D after reduction and alkylation were: A, AEK; B, C(s‐alkyl)EPGYR and WC(S‐aklyl)SPPK; CC(S‐alkyl)EHFR and C(S‐alkyl)GGK; D. C(SalkylEAFC(
s‐alkyl)I. The sequence of the 30 residue peptide is
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
An α‐helix in a peptide or protein is characterized by hydrogen bonds and characteristic dihedral angles. Choose the right combination.
Hydrogen bonding between the amide CO of residue 1 and amide NH of residue 1 + 4. Dihedral angles in the region Φ = ‐50°, ψ = ‐60º
Hydrogen bonding between amid NH of residue 1 and amide CO of residue 1 +4. Dihedral angle in the region of Φ = ‐50°, ψ = ‐60°
Hydrogen bonding between the amide CO of residue 1 and amide NH of residue 1 + 4, Dihedral angle in the region of Φ = ‐50°, ψ = +60°
Hydrogen bonding between the amide CO of residue 1 and amide NH of residue 1 + 3. Dihedral angle in the region of Φ = ‐50°, ψ = ‐60°
Precursors of the atoms in the purine skeleton are:
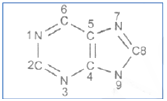
N1 Asp; C2 and C8 Formate; N3 and N9 guanidine; C4, C5 and N7 Gly; C6, CO2
N1, Asp; C2 and C8, citrage; N3 and N9 amide nitrogen of Gln, C4, C5 and N7 Gly; C6 CO2
N1 Asp; C2 and C8 formate; N3 and N9 amide nitrogen of Gln; C4, C5 and N7 Gly; C6 CO2
N1, Glu; C2 and C8 acetate; N3 and N9, mide nitrogen of Asn; C4 C5 and N7 Gly; C6 CO2
It has been observed that in 5‐10% of the eukaryotic mRNAs with multiple AUGs, the first AUG is not the initiation site. In such cases, the ribose skips over one or more AUGs before encountering the favourable one and initiating translation. This is postulated to be due to the presence of the following consensus sequence(s):
A. CCACCAUGG
B. CCGCCAUGG
C. CCGCCAUGC
D. AACGGAUGA
Which of the following sequence sets related to the above postulations is correct
A and B
A and C
C and D
B and D
The values of Tm (midpoint of denaturation), ΔHm (enthalpy change at Tm) and ΔGp (constant‐pressure heat capacity change) of protein are measured in differential canning colorimeter. ΔGp(T), the Gibbs free energy change at any temperature T(K) can be estimated using the following form of the Gibbs‐Helmholtz equation with the values obtained from these measurements:
The stability curve for the protein simulated using the observed thermodynamic values is given below:
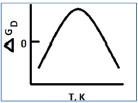
The shape of the stability curve is due to
Hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions only
Van der Waals and electrostatic interactions only
Only electrostatic interactions
Only hydrophobic interactions
Glucose is mobilized in muscle when epinephrine activates Gas. In an experiment in which muscle cells were stimulated with epinephrine, glucose mobilization was observed even after withdrawal of epinephrine. This could be
Due to the presence of a cAMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor
Very low rates of cyclic AMP formation
Due to the presence of a cAMP phosphodiesterase activator
Due the absence of protein kinase A
The dependence of the rate of sucrose uptake with respect to sucrose concentration in plant cell was studied and data are shown in the following graph. From the above data it can be inferred that:
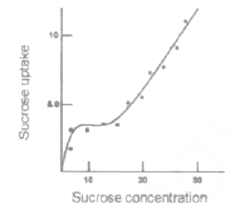
The sucrose uptake is energy independent and not special carrier is involved
The sucrose uptake is energy dependent and a special carrier is involved
At lower concentration of sucrose the uptake of sucrose is energy dependent and carrier mediated
At higher concentration of sucrose the uptake is energy dependent and carrier mediated
