 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsGiven below are names of phytohormones in column I and their associated features/ effects/ functions in column II.
| I | II |
| A. Auxin | i. Delayed leaf senescence |
| B. Gibberellins | ii. Epinastic being of leaves |
| C. Cytokinin | iii. Polar transport |
| D. Ethylene | iv. Removal of seed dormancy |
Select the correct set of combinations from the options given below:
A - iii; B - ii; C - iv; D - i
A - iv; B - iii; C - i; D - ii
A - iii; B - iv; C - i; D - ii
A - i; B - iv; C - iii; D - ii
The energy-rich fuel molecules produced in the TCA cycle are
2GTP, 2NADH and 1 FADH2
1GTP, 2NADH and 2FADH2
1GTP, 3NADH and 1FADH2
2GTP and 3NADH
The following statements are made regarding secondary metabolites of plants:
A. All secondary metabolites are constitutively produced in all cells of a plant during its entire life.
B. They serve as signals to help the plant survive adverse conditions.
C. They may be volatile compounds.
D. They contribute to flower colour.
Which one of the following options represents a combination of correct statements?
A, B, and C
B, C, and D
A, C, and D
A, B, and D
For which one of the plant hormone biosynthetic pathways, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid is an intermediate?
Abscisic acid
Brassinosteroid
Ethylene
Gibberellic acid
In a study, it was found that K+ ion concentration in root cells of a pea plant was ∼75 times greater than that of the nutrient medium in which the plant was grown. This indicated that K+ ions were absorbed from the medium
because the plant was grow continuously in the dark
by an active, energy-dependent process
by simple diffusion
through plasmodesmata connections between the epidermis and the medium
In circadian rhythm studies, following may be possible generalizations for the effectiveness of light entrainment to the day/ night cycle:
A. Shorter exposures have a greater effect than longer exposures.
B. Bright light exposures have a greater effect than dim light.
C. Intermittent light exposures have a greater effect than consistent exposures.
D. Dim light can affect entrainment relative to darkness.
Which combination of the above statements is correct?
B and C only
B and D only
A, C, and D
A, B, and D
Following are a few statements regarding the structure of terpenes:
A. Isopentenyl diphosphate and farnesyl diphosphate are monoterpene and sesquiterpene, respectively.
B. Squalene and geranyl diphosphate are triterpene and monoterpene, respectively.
C. Dimethylallyl diphosphate and gernaylgeranyl diphosphate have 10 and 20 carbon, respectively.
D. Diterpenes have 20 carbons, whereas sesquiterpenes have 15 carbons.
Which combination of the above statements is correct?
A and B
B and D
A and C
C and D
In a photoresponse experiment, imbibed seeds were kept under the following light regimes and their germination status was noted as follows:
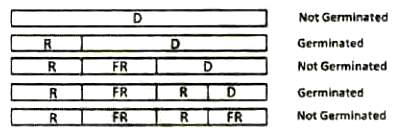
D : Darkness; R : Red light; FR : Far-red light
In an independent biochemical experiment, it was demonstrated that the red light photoreceptor phytochrome is interconverted between two forms, P and P', by red or far-red light.
Keeping this information in mind, which of the following combination of conclusions is correct?
Red light converts P to P'; P' promotes seed germination.
Far-red light converts P to P'; P' promotes seed germination.
Red light converts P' to P; P' promotes seed germination.
Far-red light converts P' to P; P promotes seed germination
The following scheme shows the flowering status of a plant species and the photoperiod regimes in which it is grown (L denotes light period; D denotes dark period).
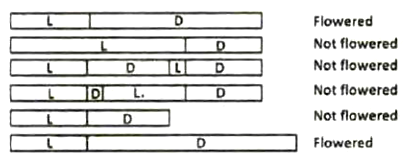
Which of the following conclusions is most appropriate?
The species is a short day plant; length of the dark phase determines flowering status.
The species is a long day plant; length of the dark phase determines flowering status.
The species is a short day plant; length of the light phase determines flowering status.
The species is a long day plant; length of the light phase determines flowering status.
Following are a few statements regarding water potential in plants:
A. Solute concentration and pressure potential contribute to water potential of a plant cell in a given state.
B. When a flaccid cell is placed in a solution that has a water potential less negative than the intracellular water potential, water will move from solution into the cell.
C. When a flaccid cell is placed in a solution that has a water potential, water will move out from cell into the solution.
D. Water potential of a plant under severe water stress is always less negative as compared to that of unstressed cells.
Which combination of the above statements is correct?
A and B
B and C
A and C
C and D
