 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn the following sequence of reactions
C2H5Br
n-propyl amine
isopropylamine
ethylamine
ethylmethyl amine
Name of method use to separate primary, secondary and tertiary amines is
Hofmann method
Lucas method
Victor Meyer method
Kolbe method
A.
Hofmann method
(a) In Hofmann method,a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amines is treated with diethyloxalate, when primary amines forms solid oxamide, secondary amines forms a liquid oxamic ester whereas tertiary amines remains unaffected.
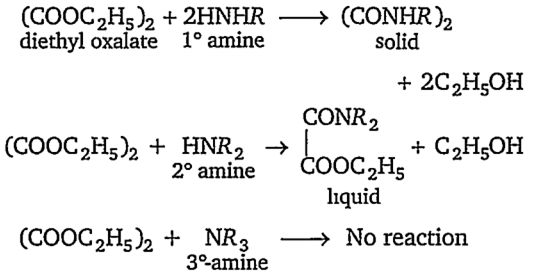
(b) With Lucas reagent, 3° alcohols immediately produce turbidity, 2° alcohols give turbidity within 5 minutes while 1° alcohols give no turbidity at room temperature.
(c) In Victor Meyer test, 1° alcohols give blood red colour, 2° alcohols give blue colour while 3° alcohols give no colour.
(d) Kolbe method is used to introduce a -COOH group in phenol.
An organic amino compound reacts with aqueous nitrous acid at low temperature to produce an oily nitroso amine. The compound is
CH3NH2
CH3CH2NH2
CH3CH2NHCH2CH3
(CH3CH2)3N
Which of the following is not a usual method for the preparation of primary amines ?
Hofmann's method
Gabriel phthalimide reaction
Curtius method
Reductive amination of >C=O
What is the product when nitrobenzene is treated sequentially with (i) NH4Cl/Zn dust and (ii) H2SO4/ Na2Cr2O7 ?
m-chloronitrobenzene
p-chloronitrobenzene
nitrosobenzene
benzene
The following species generates a highly stable radical on exposure to 100 W bulb light. Which one of the following represents this stable radical?

Me2(CN)
H3
Me2C(CN)N=
Which of the following nitro compounds are not soluble in NaOH?
(CH3)3C-NO2
(CH3)2CH-NO2
CH3CH2-NO2
Ph-CH2-NO2
The reaction,
R-CO-R RCONHR + N2 is called
Claisen-Schmidt reaction
Kolbe-Schmidt reaction
Schmidt reaction
Kolbe's reaction
