 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe bond angle is maximum in PI3,which is
| Iodide | PI3 | AsI3 | SbI3 |
| Bond angle | 102 | 100°2' | 99° |
due to small size of P
due to more bp-bp repulsion in PI3
due to less electronegativity of P
None of the above
The shape of [PtCl3(C2H4)]- and the hybridisation of Pt respectively are
tetrahedral, sp3
trigonal pyramidal, sp3
square planar, dsp2
square planar, d2sp3
C.
square planar, dsp2
Zeise's salt : [K[PtCl3(η2-C3H4)] is a -complex and square planar in structure with dsp2 hybridisation.
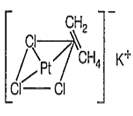
Hybridisation is [PtCl3(η2-C2H4)]-
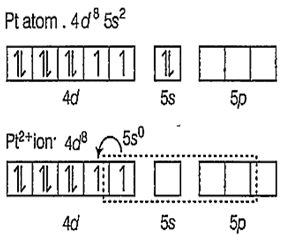
As Cl- ions and C2H4 approaches, the pairing of the unpaired electrons of d-orbitals takes place.

Among the following compounds both coloured and paramagnetic one is
K2Cr2O7
VOSO4
(NH4)2.[TiCl2]
K3[Cu(CN)4]
The number of lone pair(s) of electrons on the central atom is [BrF4]-, XeF6 and [SbCl6]3- are, respectively
2, 1 and 1
2, 1 and 0
2, 0 and 1
1, 0 and 0
The lewis acidity of BF3 is less than BCl3 even though fluorine is more electrongative than chlorine. It is due to
stronger 1p (B)-3p(Cl) σ- bonding
stronger 2p(B) - 3p(Cl) π-bonding
stonger 2p(B) - 2p(F) σ- bonding
stronger 2p(B)- 2p(F) π-bonding
The geometry around the central atom in ClF
octahedral
trigonal bipyramidal
square planar
square pyramidal
