 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe process of oxidation involve
loss of electron
gain of electron
loss of proton
loss of neutron
The number of electrons transferred when KMnO4 acts as an oxidising agent to give MnO2 and Mn2+ respectively are
2, 3
1, 5
3, 5
1, 3
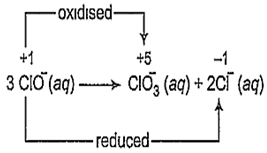
The reaction,
3ClO- (aq) → ClO (aq) + 2Cl- (aq) is an example of
oxidation reaction
reduction reaction
disproportionation reaction
decomposition reaction
C.
disproportionation reaction
A reaction in which the same species is simultaneously oxidised as well as reduced is called a disproportionation reaction. For such redox reactions to occur, the reacting species must contain an element which has atleast three oxidation states. The element in the reacting species is present in the intermediate oxidation state while the higher and lower oxidation states are available for reduction and oxidation to occur.
See the following redox reaction
A2+ + 2e- → A; E° = +0.34 V
A+ + e- → A; E° = +0.52 V
Which ion is expected to be stable?
A2+
A+
Both can form stable complexes
None can form stable complexes
A metal reacts with dil acid and liberates hydrogen. If the reduction potential of hydrogen be considered zero, the reduction potential of that metal will be
equal to its oxidation potential
positive
Zero
negative
Acidic dichromate ion reacts with hydrogen peroxide to give deep blue colour. This is due to the formation of
CrO(O)2
CrO5
Bith (a) and (b)
None of (a) and (b)
The coordination number and oxidation number X in the following compound [X(SO4)(NH3)5]Cl will be
10 and 3
2 and 6
6 and 3
6 and 4
A galvanic cell is constructed using the redox reaction,
it is represented as
Pt | H2 (g) | HCl (sol)|| AgNO3 (sol) | Ag
Ag | AgCl (s) | KCl (sol) || HCl (sol), H2 (g) | Pt
Pt | H2 (g) | KCl (sol) || AgCl (s) | Ag
Pt | H2 (g), HCl (sol) || AgCl (s) | Ag
