Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIf the direction ratio of two lines are given by l + m + n = 0, mn - 2ln + lm = 0, then the angle between the lines is
0
If (2, - 1, 3) is the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the plane, then the equation of the plane is
2x + y - 3z + 6 = 0
2x - y + 3z - 14 = 0
2x - y + 3z - 13 = 0
2x + y + 3z - 10 = 0
If the plane 3x - 2y - z - 18 = 0 meets the coordinate axes in A, B, C then the centroid of is
(2, 3, - 6)
(2, - 3, 6)
(- 2, - 3, 6)
(2, - 3, - 6)
If the direction cosines of two lines are such that l + m + n = 0, l2 + m2 - n2 = 0, then the angle between them is :
The ratio in which yz-plane divides the line segment joining ( - 3, 4, - 2) and (2, 1, 3) is
- 4 : 1
3 : 2
- 2 : 3
1 :4
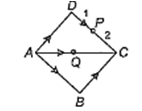
In a quadrilateral ABCD, the point P divides DC in the ratio 1 : 2 and Q is the mid point of AC. If then k is equal
- 6
- 4
6
4
A.
- 6