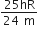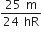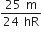Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe de-Broglie wavelength of an electron in the first Bohr orbit is
equal to half the circumference of the first orbit
equal to one fourth the circumference of the first orbit
equal to the circumference of the first orbit
equal to twice the circumference of the first orbit
Whenever a hydrogen atom emits a photon in the Balmer series, it
may emit another photon in the Paschen series
need not emit any more photon
may emit another photon in the Balmer series
must emit another photon in the Lyman series
D.
must emit another photon in the Lyman series
Balmer series lies in emission spectra.
ni = 3
nf = 2
When electron jumps from n = 3 to n = 2 and emit a photon. Then to fill of this vacancy created by an jump another from any excited state jump to n = 1 state and there by emitted a photon whose energy is equal to the difference between the two levels. After 10 sec both return to their original position. Then also emit photons process continue and we observe line spectrum.
Hence one photon emitted in Balmer seres. Then H2 atom must emit another photon in Lyman series.
In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, let R, V and E represent the radius of the orbit, the speed of electron and the total energy of the electron respectively. Which of the following quantity is proportional to the quantum number n ?
VR
RE
Given the value of rydberg constant is 10 m-1, the wave number of the last line of the Balmer series in hydrogen spectrum will be:
0.5 x 107 m-1
0.25 x 107 m-1
2.5 x107 m-1
2.5 x107 m-1
The ratio of escape velocity at earth (Ve) to the escape velocity at a planet (vp) whose radius and mean density are twice as that of earth is,
1: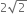
1:4
1:
1:
Consider 3rd orbit of He+ (Helium), using non-relativistic approach, the speed of electron in this orbit will be (given K= 9 x 109 constant, Z=2 and h (Planck's constant = 6.6 x 10-34 Js-1
2.92 x 106 m/s
1.46 x 106 m/s
0.73 x 106 m/s
0.73 x 106 m/s
A proton carrying 1 MeV kinetic energy is moving in a circular path of radius R in the uniform magnetic field. What should be the energy of an alpha particle to describe a circle of the same radius in the same field.
2 MeV
1 MeV
0.5 MeV
0.5 MeV
The transition from the state n = 3 to n=1 in a hydrogen-like atom results in ultraviolet radiation. Infrared radiation will be obtained in the transition from.
2→ 1
3 →2
4 → 2
4 → 2
An electron in hydrogen atom first jumps from third excited state to second excited state and then from second excited to the first excited state. The ratio of the wavelengths λ1:λ2 emitted in the two cases is
7/5
27/20
27/5
27/5
An electron of a stationary hydrogen atom passes from the fifth energy level to ground level. The velocity that the atom acquired as a result of photon emission will be