 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsHydrogen atom in ground state is excited by a monochromatic radiation of 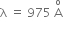 . The number of spectral lines in the resulting spectrum emitted will be,
. The number of spectral lines in the resulting spectrum emitted will be,
3
2
6
6
A certain mass of hydrogen is changed to helium the process of fusion. The mass defect in fusion reaction is 0.02866 u. The energy liberated per u is (given 1 u =931 MeV)
2.67 MeV
26.7 MeV
6.675 MeV
6.675 MeV
Ratio of longest wavelength corresponding to Lyman and Balmer series in hydrogen spectrum is
5/27
3/23
7/29
7/29
Electrons used in an electron microscope are accelerated by a voltage of 25 kV. If the voltage is increased to 100 kV then the de - Broglie wavelength associated with the electrons would
decrease by 2 times
decrease by 4 times
increase by 4 times
increase by 4 times
The wavelength of the first line of Layman series for the hydrogen atom is equal to that of the second line of Balmer series for a hydrogen-like an ion. The atomic number Z of hydrogen-like ion is
4
1
2
2
In the spectrum of hydrogen, the ratio of the longest wavelength in the Lyman series to the longest wavelength in the Balmer series is
4/9
9/4
27/5
27/5
The energy of a hydrogen atom in the ground state is -13.6 eV. The energy of a He+ ion in the first excited state will be
-13.6 eV
-27.2 eV
-54.4eV
-54.4eV
A.
-13.6 eV
Energy E of an atom with principal quantum number n is given n 
The potential difference that must be applied to stop the fastest photoelectrons emitted by a nickel surface, having work function 5.01 eV, when ultraviolet light of 200 nm falls on it, must be
2.4 V
-1.2 V
-2.4 V
-2.4 V
The electron in the hydrogen atom jumps from excited state (n=3) to its ground state (n=1) and the photons thus emitted irradiate a photosensitive material. If the work functions of the material is 5.1 eV, the stopping potential is estimated to be (the energy of the electron is nth state En = -13.6/n2 eV)
5.1 V
12.1 V
17.2 V
17.2 V
