 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsCp and Cv are specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume respectively. It is observed that
Cp – Cv = a for hydrogen gas
Cp – Cv = b for nitrogen gas
The correct relationship between a and b is
a = 14 b
a = 28 b
a = 1/14b
a = 1/14b
The speed of sound in oxygen (O2) at a certain temperature is 460 ms−1. The speed of sound in helium (He) at the same temperature will be (assumed both gases to be ideal)
1420 ms−1
550 ms−1
375 ms−1
375 ms−1
A charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to its direction. Then
the momentum changes but the kinetic energy is constant
both momentum and kinetic energy of the particle are not constant
both, momentum and kinetic energy of the particle are constant
both, momentum and kinetic energy of the particle are constant
A gaseous mixture consists of 16 g of helium and 16 g of oxygen. The ratio cp/cv of the mixture is
1.59
1.62
1.4
1.4
One mole of ideal monoatomic gas (γ = 5/30) is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas(γ = 7/5). What is γ for the mixture? γ denotes the ratio of specific heat at constant pressure, to that at constant volume.
3/2
23/15
35/23
35/23
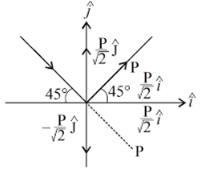
The mass of a hydrogen molecule is 3.32 x 10-27 kg. If 1023 hydrogen molecules strike, per second, a fixed wall of area 2cm2 at an angle of 45° to the normal, and rebound elastically with a speed of 103 m/s, then the pressure on the wall is nearly:
4.70 x 102 N/m2
2.35 x 103 N /m2
4.70 x 103 N/m2
2.35 x 102 N /m2
B.
2.35 x 103 N /m2
Change in momentum
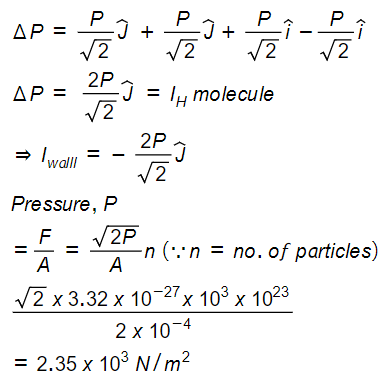
A particle is moving in a circular path of radius a under the action of an attractive potential U = -k/2r2. its total energy is:
zero
For an ideal gas, the specific heat at constant pressure Cp is greater than the specific heat at constant volume Cv. This is because
There is a finite work done by the gas on its environment when its temperature is increased while the pressure remains constant
There is a finite work done by the gas on its environment when its pressure is increased while the volume remains constant
There is a finite work done by the gas on its environment when its pressure is increased while the temperature remains constant
The pressure of the gas remains constant when its temperature remains constant
The difference between the specific heats of a gas is 4150 Jkg-1 K-1. If the ratio of specific heat is 1.4, then the specific heat at constant volume of the gas (in J kg-1 K-1) is
1037.5
2037.5
8300
10375
For a monoatomic gas, the molar specific heat at constant pressure divided by the molar gas constant R is equal to
2.5
1.5
5.0
3.5
