 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA door 1.6 m wide requires a force of 1 N to be applied at the free end to open or close it. The force that is required at a point 0.4 m distance from the hinges for opening or closing the door is
1.2 N
3.6 N
2.4 N
4 N
Two small spheres of masses M1 and M2 are suspended by weightless insulating threads of lengths L1 and L2. The spheres carry charges Q1 and Q2 respectively. The spheres are suspended such that they are in level with one another and the threads are inclined to the vertical at angles of θ1 and θ2 as shown. Which one of the following conditions is essential, if θ1 = θ2 ?
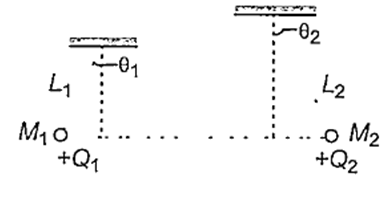
M1 ≠ M2, but Q1 = Q2
M1 = M2
Q1 = Q2
L1 = L2
A ball rests upon a flat piece of paper on a table top. The paper is pulled horizontally but quickly towards right as shown relative to its initial position with respect to the table, the ball

Hence, the correct statement is/are
Both (1) and (2)
only (3)
only (1)
only (2)
A boy throws a cricket ball from the boundary to the wicket-keeper. If the frictional force due to air cannot be ignored, the forces acting on the ball at the position X are respected by




Block A of mass of 2 kg is placed over block B of mass 8 kg. The combination is placed over a rough horizontal surface. Coefficient of friction between B and the floor is 0.5. Coefficient of friction between blocks A and B is 0.4. A horizontal force of 10 N is applied on block B. The force of friction between blocks A and Bi s (g = 10 ms-2)
100 N
40 N
50 N
Zero
The resultant of two forces acting at an angle of 120° is 10 kg-wt and is perpendicular to one of the forces. That force is
10 kg-wt
D.

A block kept on a rough surface starts sliding when the inclination of the surface is with respect to the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is
sec θ
sin θ
tan θ
cos θ
A person is driving a vehicle at uniform speed of 5 ms-1 on a level curved track of radius 5 m. The coefficient of static friction between tyres and road is 0.1. Will the person slip while taking the turn with the same speed ? Take g = 10 ms-2.
A person will slip, if v2 = 5 m2s-2
A person will slip, if v2 > 5 m2s-2
A person will slip, if v2 < 5 m2s-2
A person will not slip, if v2 > 5 m2s-2
A car moving with a velocity of 20 ms-1 stopped at a distance of 40 m. If the same car is travelling at double the velocity, the distance travelled by it for same retardation is
320 m
1280 m
160 m
640 m
