 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIn the entire path of a projectile, the quantity that remains unchanged is
vertical component of velocity
horizontal component of velocity
kinetic energy
potential energy
A block of mass 10 kg is moving horizontally with a speed of 1.5 ms-1 on a smooth plane. If a constant vertical force 10 N acts on it, the displacement of the block from the point of application of the force at the end of 4 s is
5 m
20 m
12 m
10 m
A block of weight 4 kg is resting on a smooth horizontal plane. If it is struck by a jet of water at the rate of 2 kgs-1 and at the speed of 10 ms-1, then the initial acceleration of the block is
15 ms-2
10 ms-2
5 ms-2
1 ms-2
Two projectiles A and B thrown with speeds in the ratio 1 : acquired the same heights. If A is thrown at an angle of 45° with the horizontal, the angle of projection of B will be
0°6
60°
30°
45°
A block at rest slides down a smooth inclined plane which makes an angle 60° with the vertical and it reaches the ground in t1 seconds. Another block is dropped vertically from the same point and reaches the ground in t2 seconds. Then the ratio of t1 : t2 is
1 : 2
2 : 1
1 : 3
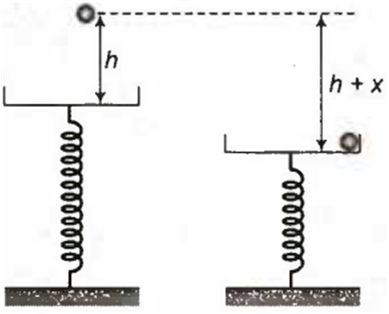
A ball of mass m is dropped from a height h on a platform fixed at the top of a vertical spring, as shown in figure. The platform is depressed by a distance x. Then the spring constant is
C.
A ring starts to roll down the inclined plane of height h without slipping. The velocity with which it reaches the ground is
The angular momentum of a particle describing uniform circular motion is L. If its kinetic energy is halved and angular velocity doubled, its new angular momentum is
4 L
2 L
The maximum height of a projectile is half of its range on the- horizontal. If the velocity of projection is u, its range on the horizontal is
