 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA coil having N turns carry a current as shown in the figure. The magnetic field intensity at point P

Zero
An electron moves at right angle to a magnetic field of 1.5×10-2 T with a speed of 6 x 107 m / s. If the specific charge of the electron is 1.7x 1011 C/ kg. The radius of the circular path will be
2.9 cm
3.9 cm
2.35 cm
2 cm
If a charge particle enters perpendicularly in the uniform magnetic field, then:
energy and momentum both remains constant
energy remains constant but momentum changes
both energy and momentum changes
energy changes but momentum remains constant
A coil in the shape of an equilateral triangle of side l is suspended between the pole pieces of a permanent magnet such that B is in plane of the coil. If due to current i in the triangle a torque T acts on it, the side l of the triangle is
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
C.
![]()
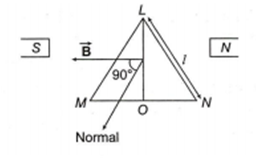
Torque acting on equilateral triangle in a magnetic field& ![]() is
is
T = i AB sinθ
Area of triangle LMN
A = 1/2 × base × height
A = 1/2 ×l × sin 60o
(since an equilateral triangle has an angle of 60o each)
![]()
Substituting the given value in expression for torque, we have
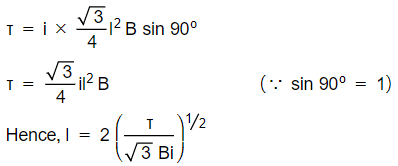
An electron moves in a circular orbit with a uniform speed v. It produces a magnetic field B at the centre of the circle. The radius of the circle is proportional, to
B/v
v/B
√v/B
√B/v
In a mass spectrometer used for measuring the masses of ions, the ions are initially accelerated by an electric potential V and then made to describe semicircular paths of radius R using a magnetic field B. If V and B are kept constant the ratio will be proportional to
R2
R
The north pole of a long horizontal bar magnet is being brought closer to a vertical conducting plane along the perpendicular direction. The direction of the induced current in the conducting plane will be
horizontal
vertical
clockwise
Anticlockwise
An electric current passes through a long straight copper wire. At a distance 5 cm from the straight wire, the magnetic field is B. The magnetic field at 20 cm from the straight wire would be
An electron of mass m and charge q is travelling with a speed v along a circular path of radius r at right angles to a uniform magnetic field B. If speed of the electron is doubled and the magnetic field is halved, then resulting path would have a radius of
2r
4r
A galvanometer acting as a voltmeter should have
low resistance in series with its coil
low resistance in parallel with its coil
high resistance in series with its coil
high resistance in parallel with its coil
