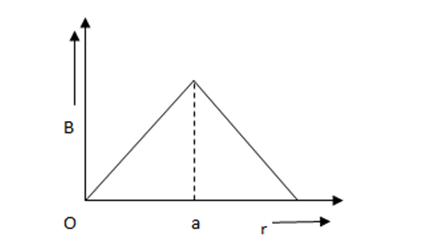
Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAssertion: When a radius of circular loop carrying current is doubled, its magnetic moment becomes four times.
Reason: Magnetic moment depends on area of the loop.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
In the following diagram, which particle has highest e/m value?
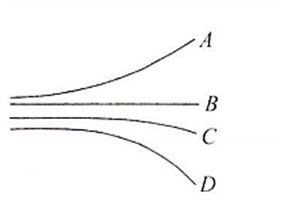
A
B
C
D
D.
D
When electron enters a region in which there is uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the velocity v, of the electric field, the electron experiences a force F with a magnitude given by following eqaution
F = e v B
The force is perpendicular to both v and B and its direction can be found by using the right-hand rule. The force will cause the electron to circular orbit with radius r ( uniform circular motion ).
We can equate the forces on the electron
⇒ e v B =
, if B and v are the same. The radius of curvature of D is minimum. Therefore is maximum.
Circular loop of a wire and a long straight wire carry currents Ic and Ie respectively as shown in figure. Assuming that these are places in the same plane, the magnetic field will be zero at the centre of the loop when separation H is

A metallic ring is dropped down, keeping its plane perpendicular to a constant and horizontal magnetic field. The ring enters the region of magnetic field at I = 0 and completely emerges out at t = T sec. The current in the ring varies as




A conducting ring of radius 1 meter is placed in a uniform magnetic field B of 0.01 tesla oscillating with frequency 100 Hz with its plane at right angle to B. What will be the induced electric field?
volts/m
2 volts/m
10 volts/m
62 volts/m
A proton and an -particle, moving with the same velocity, enter into a uniform magnetic field, acting normal to the plane of their motion. The ratio of the radii of the circular paths described by the proton -particle is
1 : 2
1 : 4
1 : 16
4 : 1
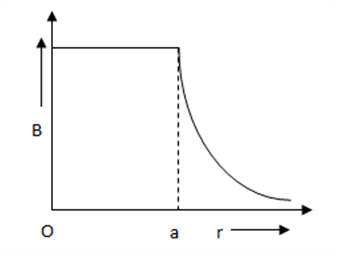
The electric field due to a uniformly charged sphere of radius R as a function of the distance from its centre is represented graphically by

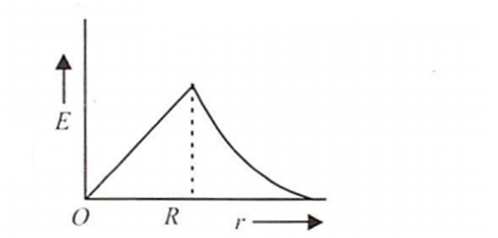
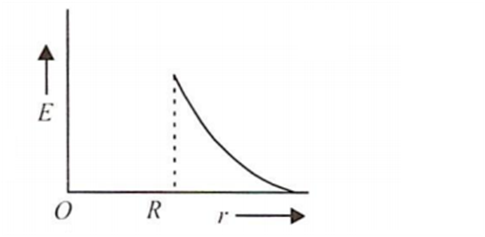

A circular coil of radius is R carries an electric current. The magnetic field due to the coil at a point on the axis of the coil located at a point on the axis of the coil located at a distance r from the centre of the coil, such that r >> R, varies as
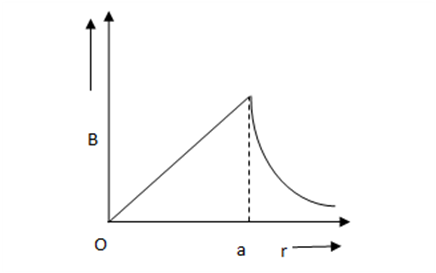
The magnetic field due to straight conductor of uniform cross-section of radius ' a ' and carrying a steady current is represented by