 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTo increase both the resolving power and magnifying power of a telescope
the focal length of the objective has to be increased
both the focal length and aperture of the objective has to be increased
the wavelength of light has to be decreased
the aperture of the objective has to be increased
B.
both the focal length and aperture of the objective has to be increased
Focal length and aperture of objective lens must be increased.
An astronomical telescope has objective eyepiece of focal lengths 40 cm and 4 cm respectively. To view an object 200 cm away from the objective lens, the lenses must be separated by a distance,
46.0 cm
50.0 cm
54.0 cm
37.3 cm
Match the corresponding entries of Column 1 with Column 2. [ where m is the magnification produced by the mirror]
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
| A. m = -2 | a. convex mirror |
| B. m = -1/2 | b. Concave mirror |
| C. m = +2 | c. Real image |
| D. m = +1/2 | d. Virtual image |
A --> a and c; B --> a and d; C --> a and b ; D --> c and d
A --> a and d; B --> b and c; C --> b and d; D --> b and c
A --> c and d; B --> b and d; C --> b and c; D --> a and d
A --> c and d; B --> b and d; C --> b and c; D --> a and d
The refracting angle of a prism is A, and the refractive index of the material of the prism is cot (A/2). The angle of minimum deviation is
180o-3A
180o-2A
90o-A
90o-A
Two identical thin plano-convex glasses lenses (refractive index 1.5) each having radius of curvature of 20 cms are placed with their convex surfaces in contact at the centre. The intervening space is filled with oil of refractive index 1.7. The focal length of the combination is
-20 cm
-25 cm
-50 cm
-50 cm
The angle of incidence for a ray of light at a refracting surface of a prism is 45o. The angle of prism is 60o. If the ray suffers minimum deviation through the prism, the angle of minimum deviation and refractive index of the material of the prism respectively, are
30o, 
45o ; 
30o; 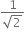
30o; 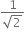
For the angle of minimum deviation of a prism to be equal to its refracting angle, the prism must be made of a material whose refractive index
Lies between 
Lies between 2 and 
is less than 1
is less than 1
A rod of length 10 cm lies along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm in such way that it end closer to pole is 20 cm away from the mirror. The length of the image is
10 cm
15 cm
2.5 cm
2.5 cm
The magnifying power of a telescope is 9. When it is adjusted for parallel rays the distance between the objective and eyepiece is 20 cm. The focal length of lenses are
10 cm, 10 cm
15 cm, 5 cm
18 cm, 2cm
18 cm, 2cm
A concave mirror of focal length f1 is placed at a distance of d from a convex lens of focal length f2. A beam of light coming from infinity and falling on this convex lens concave mirror combination returns to infinity. The distance d must be equal
f1 +f2
-f1 +f2
2f1+f2
2f1+f2
