 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA hypothetical reaction A 2B proceeds through the following sequence of steps
I. A C;
II. C D;
III. B;
The heat of hypothetical reaction is
q1 + q2 - 2q3
q1 + q2 + 2q3
q1 + 2q2 - 2q3
q1 - q2 + 2q3
Look at the graph,
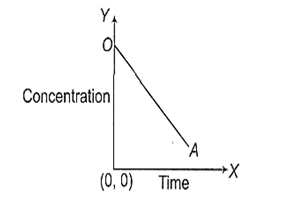
Choose the correct equation from the following which best suited to the above graph
[At] = [A]0 -Kt
[At] = [A]0 + Kt
[At] = [A0]e-Kt
[At] = Kt2 + [A0]
Observe the following reaction
2A + B C
The rate of formation of C is 2. 2 x 10-3 mol L-3 min-1. What is the value of (in mol L-1 min-1)?
Which of the following is an example for heterogeneous catalysis reaction?
2SO2(g) + O2 2SO3(g)
Hydrolysis of aqueous sucrose solution in the presence of a aqueous mineral acid
2H2O2 (l) 2H2O2(l) + O2(g)
Hydrolysis of liquid in the presence of aqueous mineral acid
A hypothetical reaction
X2 + Y2 2XY follows the following mechanism
X2 X + X .... fast
X + Y2 XY + Y .... slow
X + Y XY .... fast
The order of overall reaction is
2
1
0
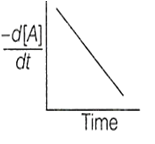
The variation of concentration of the product P with time in the reaction, A P is shown in following graph.

The graph between and time will be of the type



The average kinetic energy of an ideal gas per molecule in SI units at 25°C will be
6.17 x 10-21 JK-1
6.17 x 10-21 JK-1
6.17 x 1020 JK-1
7.16 x 10-20 JK-1
In the first order reaction, 75% of the reactant gets disappeared in 1.386 h. The rate constant of the reaction is
3.0 10-3 s-1
2.8 10 -4 s-1
17.2 10-3 s-1
1.8 10-3 s-1
2 g of a radioactive sample having half-life of 15 days was synthesised on 1st Jan 2009. The amount of the sample left behind on 1st March, 2009 (including both the days) is
0 g
0.125 g
1 g
0.5 g
