 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe top of the atmosphere is about 400 kV with respect to the surface of the earth, corresponding to an electric field that decreases with altitude. Near the surface of the earth, the field is about 100 Vm-1. Still, we do not get an electric shock as we step out of our house into the open house because (assume the house to be a steel cage so that there is no field inside)
there is a potential difference between our body and the ground
100 Vm-1 is not a high electric field so that we do not feel the shock
our body and the ground forms an equipotential surface
the dry atmosphere is not a conductor
A 30 V, 90 W lamp is to be operated on a 120 V DC line. For proper glow, a resistor of ....... Ω should be connected in series with the lamp.
40
10
20
30
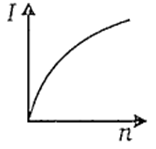
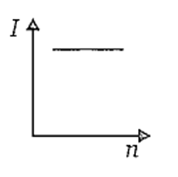
A battery consists of a variable number (n) of identical cells, each having an internal resistance r connected in series. The terminals of the battery are short-circuited. A graph of current (I) in the circuit versus the number of cells will be as shown in figure


A current of 6 A enters one corner P of an equilateral triangle PQR having 3 wires of resistances 2 Ω each and leaves by the comer R. Then the current I1 and I2 are

2 A, 4 A
4 A, 2 A
1 A, 2 A
2 A, 3 A
In the Wheatstone's network given, P = 10 Ω, Q = 20 Ω, R = 15 Ω, S =30 Ω, the current passing through the battery (of negligible internal resistance) is

0.36 A
zero
0.18 A
0.72 A
A current of 5 A is passing through a metallic wire of cross-sectional area 4 × 10-6 m2. If the density of charge carriers of the wire is 4 × 1026 m-3 the drift velocity of the electrons will be
1 × 102 ms-1
1.56 × 10-2 ms-1
1.56 × 10-3 ms-1
1 × 10-2 ms-1
Two bulbs rated 25 W-220 V and 100 W-220 V are connected in series to a 440 V supply. Then,
100 W bulb fuses
25 W bulb fuses
both the bulbs fuse
neither of the bulb fuses
The current passing through the ideal ammeter in the circuit given below is

1.25 A
1 A
0.75 A
0.5 A
A and B are two mfinitely long straight parallel conductors. C is another straight conductor of length 1 m kept parallel to A and B as shown in the figure. Then the force experienced by C is
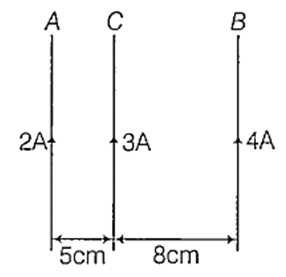
towards A equal to 0.6 × 10-5 N
towards B equal to 54 × 10-5 N
towards A equal to 5.4 × 10-5 N
towards B equal to 0.6 × 10-5 N
The resultant force on the current loop PQRS due to a long current carrying conductor will be
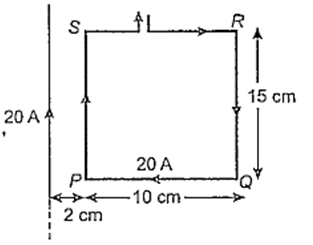
10-4 N
3.6 × 10-4 N
1.8 × 10-4 N
5 × 10-4 N
