 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo equal resistances R are joined with voltage source V in (i)series (ii)parallel, the ratio of electrical power consumed in two cases will be
1:4
4:1
2:1
1:2
A.
1:4
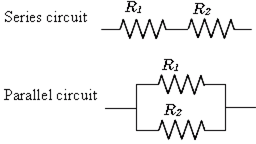
(a)The same current flows through each part of a series circuit. The total resistance a series circuit is equal to the sum of individual resistances. Voltage applied to a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drop. Two resistors are said to be if only one of the endpoints is closed.
In series:- total resistance= R+R=2R
(b)Two or more resistors are said to be in parallel if one end of all the resistors is joined together and similarly the other ends joined together.
In parallel:- potential difference across each resistance will be V
So, power consumed in each resistance is
When a resistance of α Ω is connected at the ends of a battery, its potential difference decreases from 40 V to 30V. The internal resistance of the battery is
3Ω
6Ω
1.5Ω
4Ω
The equivalent resistance and potential difference between A and B for the circuit
respectively are
4Ω, 8V
8Ω, 4V
2Ω, 2V
16Ω, 2V
A wire of resistance R is divided in equal parts, then these parts are joined in parallel, the equivalent resistance of the combination will be
nR
When a certain current is passed in the circuit as shown in figure, 10 kcal of heat is produced in 5 Ω resistance. How much heat is produced in 4 Ω resistance?

4 kcal
2 kcal
5 kcal
3 kcal
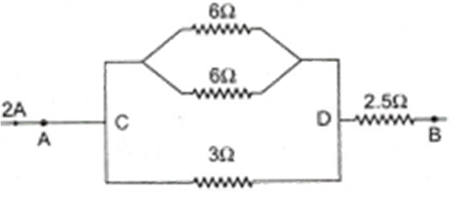
In the given circuit, what will be the equivalent resistance between the points A and B ?

10 / 3 Ω
20 / 3 Ω
10 / 5 Ω
5 Ω
A uniform wire of length I and having resistance R is cut into n equal parts and all parts are connected in parallel, then the equivalent resistance will be :
R
R/n
R/n2
n2R
When a wire of uniform cross-section a, length land resistance R is bent into a complete circle, resistance between two of dimetrically opposite points will be
4R
