 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich of the following figures represents the variation of the particle momentum and associated de-Broglie wavelength?
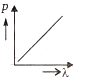

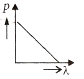
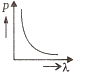
A and B are two metals with threshold frequencies 1.8 x 1014 Hz and 2.2 1014 Hz. Two identical photons of energy 0.825 eV each are incident on them. Then photoelectrons are emitted by (Take h = 6.6 x 10-34 J-s)
B alone
A alone
Neither A nor B
Both A and B
The emission electron is possible by
photoelectric effect
thermionic effect
both (a) and (b)
none of the above
An electron and a proton are possessing the same amount of kinetic energies. The de-Broglie wavelength is greater for :
electron
proton
both same
none of these
If the work function of a metal is 4.2 eV, the cut-off wavelength is :
8000 Å
7000 Å
1472 Å
2950 Å
The wavelength of light coming from a distant galaxy is found to be 0.5% greater than the wavelength of light coming from a stationary source. The galaxy is
coming towards earth with velocity of light
moving away from earth with velocity 1.5 x 106 m/sec
stationary with respect to earth
moving away from earth with velocity of light
Wave nature of light does not explain
Interference
Total internal reflection
Photo-electric effect
Refraction
The light of frequency v falls on a certain photoelectric substance of threshold frequency v0. The work function of the substance is
hv0
hv
h(v - v0)
The energy of a photon corresponding to the visible light of maximum wavelength is approximately
1 eV
1.6 eV
3.2 eV
7 eV
The rest mass of the photon is
zero
infinite
between zero and infinite
equal to that of electron
A.
zero
The concept of the rest mass derives from special relativity. The rest mass is the mass of a particle (in our case the photon) as measured by an observer who sees the particle still and with zero speed.
