 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAssertion: Thin films such a soap bubble or a thin layer of oil on water show beautiful colours when illuminated by white light.
Reason: It happens due to the interference of light reflected from upper surface of the thin film.
If both the assertion and reason are true and reason is a correct explanation of assertion.
If both assertion and reason are true but assertion is not a correct explanation of the assertion.
If both the assertion is true but the reason is false.
If both assertion and reason are false.
For liquid to rise in a capillary tube, the angle of contact should be
acute
obtuse
right
none of these
A.
acute
When impure water or kerosene is taken in a glass vessel, it is found that the surface near the walls is curved concave upwards.
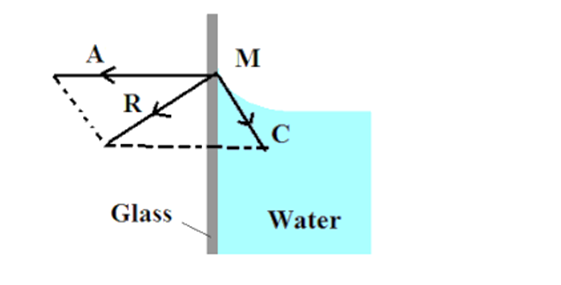
Consider a molecule of water M on the free surface close to the wall of the glass vessel. The magnitude of adhesive force A is greater than the magnitude of cohesive force C and resultant of the two molecular forces of attraction R is or outside the liquid. Hence the molecule A is attracted towards the walls of glass vessel. The free surface of water adjust itself at right angle to the resultant R. Therefore molecules like M creep upwards and the angle of contact is acute.
Which of the following physical wuantity do not have same dimensions?
pressure and stress
tension and surface tension
strain and angle
energy and work
The length of a needle floating on water is 2.5 cm. Calculate the added force (due to surface tension) required to pull the needle out of water. (Surface tension of water = 7.2 10-2 N/m2)
3.6 10-3 N
3.4 10-10 N
3.0 10-5 N
3.8 10-11 N
A capillary tube of radius r is immersed in water and water rises in it to a height H. Mass of water in the capillary tube is m. If the capillary of radius 2r is taken and dipped in water, the mass of water that will rise in the capillary tube will be
m
2 m
m/2
4 m
The work done in increasing the size of a soap film from 10 cm x 6 cm to 10 cm x 11 cm is 3 x 10-4 J. The surface tension of the film is
1.5 × 10-2 N/m
3 × 10-2 N/m
6.0 × 10-2 N/m
11 × 10-2 N/m
The maximum force in addition to the weight required to pull a wire 5.0 cm long from the surface of the water at temperature 20°C, is 728 dyne. The surface tension of water is
7.28 N/cm
7.28 dyne/cm
72.8 dyne/cm
7.28 × 102 dyne/cm
If work done in increasing the size of a soap film from 10 cm x 6 cm to 10 cm x 11 cm is 2x10-4 J, then surface tension is
2x10-2 Nm-1
2x10-4 Nm-1
2x10-6 Nm-1
2x10-8 Nm-1
At which of the following temperatures, the value of surface tension of water is minimum
4º C
25º C
50º C
75º C
Work done in splitting a drop of water of 1 mm radius into 64 droplets is (surface tension of water = 72x 10-3 J/m2)
2.0 x 10-6 J
2.7 x 10-6 J
4 x 10-6 J
5.4 x 10-6 J
