 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA proton, a deuteron and an α-particle having the same kinetic energy are moving in circular trajectories in a constant magnetic field. If rp, rd and rα denote respectively the radii of the trajectories of these particles, then
rα = rd > rp
rα = rd = rp
rα < rd < rp
rα = rp > rd
A solenoid has core of a material with relative permeability 500 and its windings carry a current of 1 A. The number of turns of the solenoid is 500 m-1. The magnetization of the material is nearly
2.5 × 103 Am-1
2.5 × 105 Am-1
2.0 × 103 Am-1
2.0 × 105 Am-1
B.
2.5 × 105 Am-1
Given, µr = 500, i = 1 and n = 500
Intensity of magnetisation
I = χmH
= (µr − 1) ni
= (500 − 1) × 500 × 1
= 499 × 500 × 1
= 2.495 × 105
= 2.5 × 105 A/m
A 2 µC charge moving around a circle with a frequency of 6.25 x 1012 Hz produces a magnetic field 6.28 T at the centre of the circle. The radius of the circle is
2.25 m
0.25 m
13.0 m
1.25 m
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω is converted to a voltmeter of range 10 V by connecting a resistance of 10 kΩ. The resistance required to convert the same galvanometer to an ammeter of range 1 A is
0.4 Ω
0.3 Ω
0.1 Ω
0.2 Ω
Two wires with currents 2 A and 1 A are enclosed in a circular loop. Another wire with current 3 A is situated outside the loop as shown. Then around the loop is
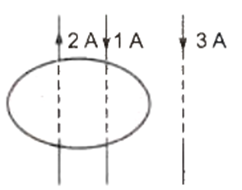
µ0
3 µ0
6 µ0
2 µ0
A current I enters a circular coil of radius R, branches into two parts and then recombines as shown in the circuit diagram
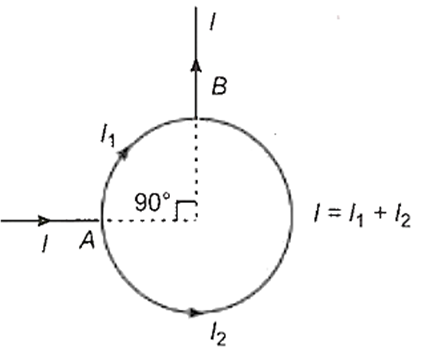
The resultant magnetic field at the centre of the coil is
zero
The resistance of a galvanometer is 50 Ω and it shows full scale deflection for a current of 1 mA. To convert it into a voltmeter to measure 1 V and as well as 10 V (Refer circuit diagram) the resistances R1 and R2 respectively are
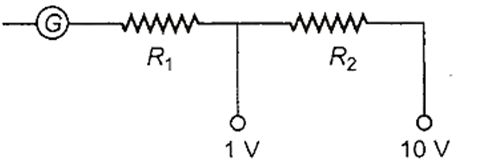
950 Ω and 9150 Ω
900 Ω and 9950 Ω
900 Ω and 9900 Ω
950 Ω and 9000 Ω
Two long parallel wires carry currents i1 and i2 such that i1 >i2. When the currents are in the same direction, the magnetic field at a point midway between the wires is 6 x 10-6 T. If the direction of i2 is reversed, the field becomes 3 x 10-5 T. The ratio is
2
A coil of 100 turns and area 2 x 10-2 m2, pivoted about a vertical diameter in a uniform magnetic field carries a current of 5A. When the coil is held with its plane in North-South direction, it experiences a torque of 0. 3 Nm. When the plane is in East-West direction the torque is 0.4 Nm. The value of magnetic induction is (Neglect earth's magnetic field)
0.2 T
0.3 T
0.05 T
0.1 T
Two particles of equal charges after being accelerated through the same potential difference enter a uniform transverse magnetic field and describe circular path of radii R1 and R2 respectively. Then the ratio of their masses (M1/M2)
(M,/M,) i
