 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo thin equiconvex lenses each of focal length 0.2 m are placed coaxially with their optic centres 0.5 m apart. Then the focal length of the combination is
− 0.4 m
0.4 m
− 0.1 m
0.1 m
A prism of a certain angle deviates the red and blue rays by 8° and 12° respectively. Another prism of the same angle deviates the red and blue rays by 10° and 14° respectively. The prisms are small angled and made of different materials. The dispersive powers of the materials of the prisms are in the ratio
5 : 6
9 : 11
6 : 5
11 : 9
A 20 cm length of a certain solution causes right handed rotation of 38°. A 30 cm length of another solution causes left handed rotation of 24°. The optical rotation caused by 30 cm length of a mixture of the above solutions in the volume ratio 1 : 2 is
left handed rotation of 14°
right handed rotation of 14°
left handed rotation of 3°
right handed rotation of 3°
Blue colour of sea water is due to
interference of sunlight reflected from the water surface
scattering of sunlight by the water molecules
image of sky in water
refraction of sunlight
B.
scattering of sunlight by the water molecules
Blue colour of sea water is due to scattering of sunlight by water molecules.
A ray of light enters from a rarer to a denser medium. The angle of incidence is i. Then the reflected and refracted rays are mutually perpendicular to each other. The critical angle for the pair of media is
sin-1 (tan i)
tan-1 (sin i)
sin-1 (cot i)
cos-1 (tan i)
A fish in water (refractive index n) looks at a bird vertically above in the air. If y is the height of the bird and x is the depth of the fish from the surface, then the distance of the bird as estimated by the fish is
x + ny
Figure shows a mixture of blue, green and red coloured rays incident normally on a right angled prism. The critical angles of the material of the prism for red, green and blue are 46°, 44° and 43° respectively. The arrangement will separate
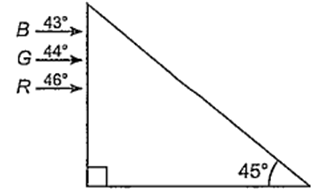
red colour from blue and green
blue colour from red and green
green colour from red and blue
all the three colours
A convex and a concave lens separated by distance d are then put in contact. The focal length of the combination
decreases
increases
becomes 0
remains the same
A convex lens is made of 3 layers of glass of 3 different materials as in the figures. A point object is placed on its axis. The number of images of the object are
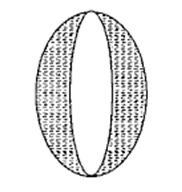
1
2
3
4
A convex lens made of glass has focal length 0.15 m in air. Ifthe refractive index of glass is and that of water is , the focal length of lens when immersed in water is
0.45 m
0.15 m
0.30 m
0.6 m
