 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe temperature, at which centigrade and Fahrenheit scales give the same reading, is
- 40°
40°
- 30°
30°
A brass rod of length 500 mm and diameter 3 mm is joined to a steel rod of same length and diameter at 50°C. If the coefficients of linear expansion of brass and steel are 2.5 x 10-5 ° C-1 and 1.25 x 10-5 ° C-1 , then change in length of the combined rod at 200°C is
2.4 mm
2.8 mm
3.2 mm
3.6 mm
A copper block of mass 4 kg is heated in a furnance to a temperature 425°C and then placed on a large ice block. The mass of ice that will melt in this process will be (Specific heat of copper = 500 J kg-1 ° C-1 and heat of fusion of ice = 336 kJ kg-1 )
0.5 kg
1 kg
1.5 kg
2.5 kg
D.
2.5 kg
Fall in temperature of copper block when it is placed on the ice block = AT = 425 − 0 = 425° C. Heat lost by copper block when it is placed on the ice block
Q1 = m1s ΔT
= 4 × 500 × 425 = 850 kJ
Heat gained by ice in melting into m2 Kg of water.
Q2 = m2L
= m2 × 336
= 336 m2 kJ
According to calorimetry principle,
heat lost = heat gained
i.e, 850 = 336 m2
∴ m2 =
= 2.5 kg
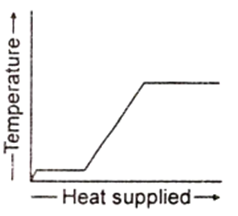
A block of ice at - 10°C is slowly heated and converted to steam at 100°C. Which of the following curves represents this phenomenon qualitatively ?
In which mode of transmission, the heat waves travel along straight line with the speed of light?
thermal radiation
forced convection
natural convection
thermal conduction
Consider a compound slab consisting of two, different materials having equal lengths, thicknesses and thermal conductivities K and 2 K respectively. The equivalent thermal conductivity of the slab is
3 K
An ideal black body at room temperature is thrown into a furnance. It is observed that
it is the darkest body at all times
it cannot be distinguished at all times
initially it is the darkest body and later it becomes brightest
initially it is the darkest body and later it cannot be distinguished
If temperature of the sun were to increase from T to 2 T and its radius from R to 2R, then how many times the radiant energy will be received on the earth ?
4
16
32
64
A black body has a wavelength of λ at temperature 2000 K. Its corresponding wavelength at temperature 3000 K will be
An ice box made of Styrofoam (Thermal conductivity = 0.01Jm-1 s-1 K-1 ) is used to keep liquids cool. It has a total wall area including lid of 0.8 m and wall thickness of 2.0 cm. A bottle of water is placed in the box and filled with ice. If the outside temperature is 30°C the rate of flow of heat into the box is (in J-s-1 )
16
14
12
10
