 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA wave of frequency 500 Hz travels with a speed of 360 ms-1. The distance between two nearest points which are 60° out of phase is
12 cm
18 cm
50 cm
24 cm
The apparent frequency observed by a moving observer away from a stationary source is 20% less than the actual frequency. If the velocity of sound in air is 330 ms-1, then the velocity of the observer is
660 ms-1
330 ms-1
66 ms-1
33 ms-1
A string under tension of 129.6 N produces 10 beats/second, when it vibrates along with a tuning fork. When the tension in the string is increased to 160 N, it vibtrates in unison with the tuning fork. Then, frequency of the tuning fork is
100 Hz
110 Hz
90 Hz
220 Hz
The ionospheric layer acts as a reflector for the frequency range
1 kHz to 10 kHz
3 to 30 MHz
3 to 30 kHz
100 kHz to 1 MHz
Two travelling waves, y1 = A sin [k(x + ct)] and y2 = A sin [k(x- ct)] are superposed on a string. The distance between adjacent antinodes is
If a stretched wire is vibrating in the second overtone, then the number of nodes and antinodes between the ends of the string are respectively
2 and 2
1 and 2
3 and 4
2 and 3
Pick out the correct statement in the following with reference to stationary wave pattern
In a tube closed at one end, all the harmonics are present
In a tube open at one end, only even harmonics are present
The distance between successive nodes is equal to the wavelength
In a stretched string, the first overtone is the same as the second harmonic
D.
In a stretched string, the first overtone is the same as the second harmonic
f2 = 2 f1 = First overtone or second harmonic
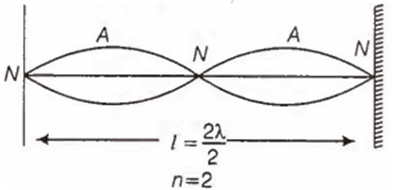
where f1 = fundamental tone or first harmonic.
In the sretched string, the first overtone is the same as the second harmonic.
So,option (d) is correct.
The bulk modulus of a liquid of density 8000 kgm-3 is 2 x 109 Nm-2. The speed of sound in that liquid is (in ms-1)
200
250
500
350
The vibrations of a string of length 60 cm fixed at both the ends are represented by the equation , where x and y are in cm. The maximum number of loops that can be formed in it, is
6
16
5
15
The pressure variations in the propagation of sound waves are
isobaric
isochoric
isobaric and isochoric
adiabatic
