 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsOn selling 17 balls at ₹ 720, there is a loss equal to the cost price of 5 balls. The cost price (in ₹) of a ball is
45
50
55
55
Two items A and B are sold at a profit of 10% and 15% respectively. If the amount of profit received is the same, then the cost price of A and B may be
₹ 1,000, ₹ 1,500
₹ 5,000, ₹ 2,000
₹ 3,000, ₹ 2,000
₹ 3,000, ₹ 2,000
Sourav purchased 30 kg of rice at the rate of ₹ 10 per kg and 35 kg at the rate of ₹ 11 per kg. He mixed the two. At what price per kg (in ₹) should he sell the mixture to make a 30% profit in the transaction?
12.5
13
13.7
13.7
Gita buys a plot of land for ₹ 96,000. She sells 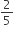 of it at a loss of 6%. She wants to make a profit of 10% on the whole transaction by selling the remaining land. The gain % on the remaining land is
of it at a loss of 6%. She wants to make a profit of 10% on the whole transaction by selling the remaining land. The gain % on the remaining land is
20

14
14
While selling, a businessman allows 40% discount on the marked price and there is a loss of 30%. If it is sold at the marked price, profit percent will be
10%
20%


By selling an article at  of the marked price, there is a gain of 25%. The ratio of the marked price and the cost price is
of the marked price, there is a gain of 25%. The ratio of the marked price and the cost price is
5 : 3
3 : 5
3 : 4
3 : 4
Successive discounts of 10%, 20% and 50% will be equivalent to a single discount of
36%
64%
80%
80%
A retailer offers the following discount schemes for buyers on an article.
I. Two successive discounts of 10%
II. A discount of 12% followed by a discount of 8%.
III. Successive discounts of 15% and 5%
IV. A discount of 20%.
The selling price will be minimum under the scheme.
I
II
III
III
By selling 100 oranges, a vendor gains the selling price of 20 oranges. His gain percent is
20
25
30
30
B.
25
S.P. of 100 Oranges - C.P. of 100 Oranges = S.P. of 20 Oranges
S.P. of 80 Oranges = C.P. of 100 Oranges
Shortcut Method: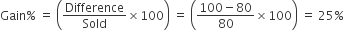
A man buys two chairs for a total cost of ₹ 900. By selling one for  of its cost and the other for
of its cost and the other for  of its cost, he makes a profit of ₹ 90 on the whole transaction. The cost of the lower priced chair is
of its cost, he makes a profit of ₹ 90 on the whole transaction. The cost of the lower priced chair is
₹ 360
₹ 400
₹ 420
₹ 420
