CBSE
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions )2 હોય, તો ......
)2 હોય, તો ......
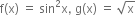
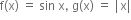
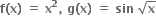
f અને g નિશ્વિત ન કરી શકાય.
1 +
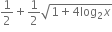
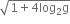
અસ્તિત્વ ધરાવતું નથી
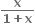 હોય, તો f એ ......... .
હોય, તો f એ ......... .
એક-એક તથા વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય છે.
એક-એક વિધેય નથી પરંતુ વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય છે.
એક-એક નથી તથા વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય પણ નથી
એક-એક વિધેય છે પરંતુ વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય નથી
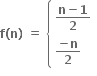
એક-એક નથી તથા વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય પણ નથી.
એક-એક વિધેય છે પરંતુ વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય નથી.
વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય છે પરંતુ એક-એક વિધેય નથી.
એક-એક તથા વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય છે.
D.
એક-એક તથા વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય છે.
Tips: -
(i) જો n1 તથા n2 અયુગ્મ હોય, તો ધારો કે f(n1) = f(n2)
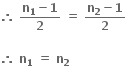
(ii) જો n1તથા n2 યુગ્મ હોય, તો ધારો કે f(n1) = f(n2)
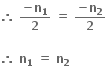
(iii) હવે જોઈએ કે n1 તથા n2 પૈકી કોઈ એક યુગ્મ તથા અન્ય અયુગ્મ હોય, તે શક્ય નથી.
n1અયુગ્મ તથા n2 યુગ્મ હોય, તો 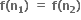 માટે
માટે 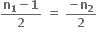
∴ n1 + n2 = 1 જે શક્ય નથી.
તે જ રીતે n1 યુગ્મ તથા n2 અયુગ્મ પણ શક્ય નથી.
ટુંકમાં 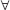 n1, n2 ∈ N; f(n1) = f(n2) ⇒ n1 = n2
n1, n2 ∈ N; f(n1) = f(n2) ⇒ n1 = n2
∴ f એક-એક વિધેય છે.
હવે, 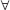 y, y ∈ જો અનૃણ હોય તો, 2y + 1 અયુગ્મ હોવાથી, f(2y + 1) =
y, y ∈ જો અનૃણ હોય તો, 2y + 1 અયુગ્મ હોવાથી, f(2y + 1) = 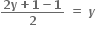
તથા y ઋણ હોય તો 2y યુગ્મ હોવાથી, 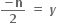 તથા n = -2y મળે.વળી
તથા n = -2y મળે.વળી 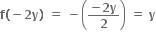
આથી, 2y + 1 અયુગ્મ પૂર્ણાંક જ હોવાથી, તથા 2y યુગ્મ પૂર્ણાંક હોવાથી, f(n) = y થાય જ.
આથી f વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય છે.
ટુંકમાં f એક-એક તથા વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય છે.
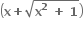 એ .........
એ .........
અયુગ્મ વિધેય છે.
યુગ્મ કે અયુગ્મ વિધેય નથી.
યુગ્મ વિધેય છે.
આવર્તી વિધેય છે.
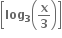 નો મહત્તમ પ્રદેશ ............ છે.
નો મહત્તમ પ્રદેશ ............ છે.
[1, 9]
(1, 9)
[9, 1]
[-1, 9]
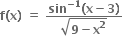 નો મહત્તમ પ્રદેશ ....... હોય.
નો મહત્તમ પ્રદેશ ....... હોય.
[3, 2]
[2, 1]
[2, 3)
[1, 2]
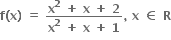 નો વિસ્તાર ....... હોય.
નો વિસ્તાર ....... હોય.
(1, ∞)
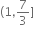
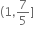
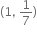

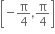
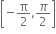
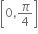
સંમિત સંબંધ નથી
સ્વવાચક સંબંધ છે.
પરંપરિત સંબંધ છે.
કોઈ સંબંધ નથી.