CBSE
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questionsસમાંતર
3
1
2
-2
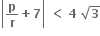
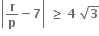
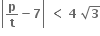
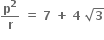
 હોય તો p = .......; q = ..........
હોય તો p = .......; q = ..........
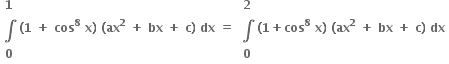 હોય, તો દ્વિઘાત સમીકરણ ax2 + bx + c = 0 ને ......... .
હોય, તો દ્વિઘાત સમીકરણ ax2 + bx + c = 0 ને ......... .
C.
Tips: -
ધારો કે વિધેય,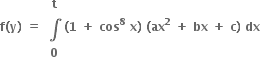 છે.
છે.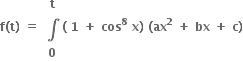
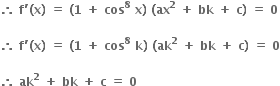
∴ k એ દ્વિઘાત સમીકરણ ax2 + bx + c = 0 નું એક બીજ થાય.
પરંતુ k ∈ (1, 2) હોવાથી, દ્વિઘાત સમીકરણ ax2 + bx + c = 0 ને (1, 2) માં ઓછામાં ઓછું એક બીજ હોય જ.