CBSE
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions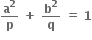
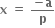
આપેલ પૈકી એક પણ નહી
 હોય તથા
હોય તથા 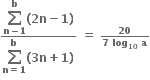 હોય તો a = ...... .
હોય તો a = ...... . 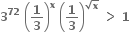 હોય તો x ∈ ........ .
હોય તો x ∈ ........ .
વાસ્ત્વવિક અસમાન
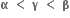
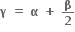
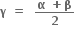
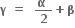
બે સમાન અને વાસ્તવિક
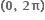

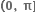
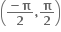
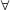 x ∈ R માટે જો દ્વિઘાત બહુપદી f(x) = ax2 + bx + c > 0 હોય તો g(x) = f(x) + f'(x) + f"(x) ....... થાય. x ∈ R.
x ∈ R માટે જો દ્વિઘાત બહુપદી f(x) = ax2 + bx + c > 0 હોય તો g(x) = f(x) + f'(x) + f"(x) ....... થાય. x ∈ R.D.
g(x) > 0Tips: -
અહીં f(x) = ax2 + bx + c > 0 આપેલ છે.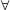 x ∈ R
x ∈ R