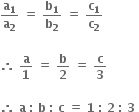CBSE
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions3
2
1
0
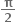 , હોય તથા સમીકરણ ax2 + bx + c = 0 (જ્યાં a ≠0)) નાં બીજ tan
, હોય તથા સમીકરણ ax2 + bx + c = 0 (જ્યાં a ≠0)) નાં બીજ tan  તથા
તથા  હોય, તો નીચેનામાંથી કયું સત્ય બને ?
હોય, તો નીચેનામાંથી કયું સત્ય બને ? 1 તથા 2 ની વચ્ચે
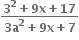 ની મહત્તમ કિંમત ........ હોય.
ની મહત્તમ કિંમત ........ હોય.
1
1/4
17/7
41
B.
1 : 3 : 2Tips: -
x2 + 2x + 3 = 0