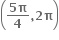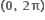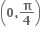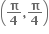CBSE
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions(b - c) f(a) + (c - b) f(b) > (c - a) f(c)
(b - a) f(c) + (c - b) f(a) > (c - a) f(b)
(b - a) f(c) + (c - b) f(a) < (c - a) f(b)
(b - c) f(a) + (c - b) f(b) > (c - a) f(c)
વિધેય f : (0, ∞) → (0, ∞) માટે,
(1) f(ab) = f(a) f(b) અને
(2)  f(x) = c, (જ્યાં ક # 0) પ્રકારનું છે. f(4) = ....
f(x) = c, (જ્યાં ક # 0) પ્રકારનું છે. f(4) = ....
1
2
3
4
FTFT
TTFF
TFTT
FTTF
D.
FTTF
Tips: -
x1, x2 ∈ B માટે g(x1) = g(x2) ⇒f(g(x)) = f(g(x)) ⇒ x1 = x2 ⇒ g એક-એક વિધેય છે.
વળી, સ્પષ્ટ જોઈ શકાય છે કે f એ વ્યાપ્ત વિધેય છે.
(f ડાબી બાજુનો પ્રતીપ હોવાથી એક-એક ના હોઈ શકે.)
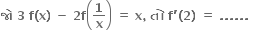
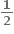
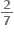
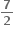
2
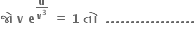
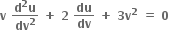
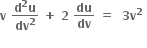
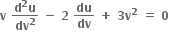
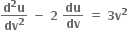
q
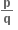
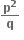
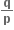

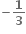

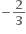

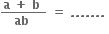
0
1
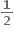
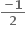
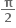

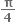

f(x) = sin x + cos x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 એ ...... અંતરાલમાં ચુસ્ત ઘટતું વિધેય છે.
એ ...... અંતરાલમાં ચુસ્ત ઘટતું વિધેય છે.