CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Every substance has unique or characteristic properties. These properties can be classified into two categories – physical properties and chemical properties.
Physical properties are those properties which can be measured or observed without changing the identity or the composition of the substance. E.g. colour, odour, melting point, boiling point, density etc. The measurement or observation of chemical properties requires a chemical change to occur. E.g. Burning of Mg-ribbon in the air.
Chemical properties are characteristic reactions of different substances; these include acidity or basicity, combustibility etc. Many properties of matter such as length, area, volume, etc., are quantitative in nature. Metric System was based on the decimal system.
Mass:
Weight:
Volume: Volume has the units of (length)3. So volume has units of m3 or cm3 or dm3. A common unit, litre (L) is not an SI unit; it is used for measurement of the volume of liquids. 1 L = 1000 mL, 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3.
Density: Density of a substance is its amount of mass per unit volume. SI unit of density = SI unit of mass/SI unit of volume = kg/m3 or kg m–3. This unit is quite large and a chemist often expresses density in g cm–3.
The International System of Units (in French Le Systeme International d‘Unites– abbreviated as SI) was established by the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM from ConferenceGenerale des Poids at Measures). The SI system has seven base units:
| PHYSICAL QUANTITY | NAME OF UNIT | ABBREVIATION |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | Kilogram | kg |
| Length | Meter | m |
| Time | Second | s |
| Temperature | Kelvin | K |
| Amount of Substance | Mole | mol |
| Electric Current | Ampere | A |
| Luminous Intensity | Candela | cd |
Derived Quantity
| DERIVED QUANTITY | NAME | ABBREVIATION |
|---|---|---|
| Area | Square Meter | m2 |
| Volume | Cubic Meter | m3 |
| Mass Density | Kilogram Per Cubic Meter | kg/m3 |
| Specific Volume | Cubic Meter Per Kilogram | m3/kg |
| Celsius Temperature | degree Celsius | oC |
Prefix
Metric units use a prefix, used for conversion from or to an SI unit. Below is a chart illustrating how prefixes are labelled in metric measurements.
| SYMBOL | PREFIX | MULTIPLICATION FACTOR |
|---|---|---|
| T | Tera | 1012 |
| G | Giga | 109 |
| M | Mega | 106 |
| k | Kilo | 103 |
| h | Hecto | 102 |
| da | Deka | 101 |
| d | Deci | 10-1 |
| c | Centi | 10-2 |
| m | Milli | 10-3 |
| µ | Micro | 10-6 |
| n | Nano | 10-9 |
| p | Pico | 10-12 |
Temperature
Temperature is usually measured in Celsius (although the U.S. still uses Fahrenheit), but is often converted to for the absolute Kelvin scale for many chemistry problems.
For Fahrenheit to Celsius: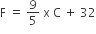
For Celsius to Fahrenheit: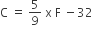
For Celsius to Kelvin:
K=C+273.15(3)
Reference Points:
Melting Point of ice is 0° C = 32° F
Boiling Point of water is 100° C = 212° F
The Kelvin scale does not use the degree symbol (°) and only K, which can only be positive since it is an absolute scale