CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
The word ‘stoichiometry’ is derived from two Greek words - stoicheion (meaning element) and metron (meaning measure).
Stoichiometry deals with the calculation of masses (sometimes volumes also) of the reactants and the products involved in a chemical reaction.
The reactant which gets consumed first or limits the amount of product formed is known as limiting reagent.
In other words, The reactant which is present in the lesser amount gets consumed after some time and after that, no further reaction takes place whatever be the amount of the other reactant present. Hence, the reactant which gets consumed limits the amount of product formed and is, therefore, called the limiting reagent.
The concentration of a solution or the amount of substance present in its given volume can be expressed in any of the following ways.
Mass Percent is the mass of the solute in grams per 100 grams of the solution.
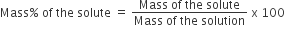
A 5 % solution of sodium chloride means that 5 g of NaCl is present in 100g of the solution.
Volume percent is the number of units of volume of the solute per 100 units of the volume of solution.

A 5 % (v/v) solution of ethyl alcohol contains 5 cm3 of alcohol in 100 cm3 of the solution.
Mole Fraction is the ratio of a number of moles of one component to the total number of moles (solute and solvents) present in the solution. It is expressed as 'x'.

Mole fraction of the solute + Mole fraction of solvent = 1
Molarity of the solution is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved per litre (dm3) of the solution. It is denoted by the symbol M. Measurements in Molarity can change with the change in temperature because of solutions expand or contract accordingly.

The Molarity of the solution can also be expressed in terms of mass and molar mass
Molarity of the solution =

In terms of weight, the molarity of the substance can be expressed as:
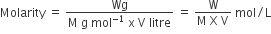
Molality- Molality is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved per 1000 g (1 kg) of solvent. Molality is expressed as 'm'.
