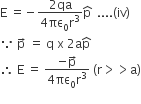CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
A uniform electric field has constant magnitude and fixed direction. Such a field is produced between the plates of a charged parallel plate capacitor.
When two charges in a dipole are separated by some distance, the forces acting at different points result in a torque on the dipole.The torque tries to align the dipole with an electric field. Once aligned, the torque becomes 0.

Magnitude of torque
τ = qE x 2a sinθ
τ = 2qaE sinθ
τ = pEsinθ.
The vector form of torque is the cross product of dipole moment and electric field.
The magnitudes of the electric field due to the two charges +q and -q are given by,

The directions of E+q and E-q are as shown in the figure. The components normal to the dipole axis cancel away. The components along the dipole axis add up.
Therefore, Total electric field.
E = - (E+q + E-q) cosθ p [Negative sign shows that field is opposite to p]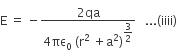
At large distances (r>>a),this reduces to