CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
An electric dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges q and –q separated by a (small) distance 2a. Its total charge is zero.

The potential due to the dipole is,
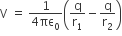
Taking r1 and r2 = r2+ a2 ± 2arcosθ
r>>a
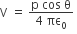
where p =2qa
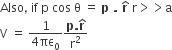
(Positive sign for θ = 0, negative sign for θ = π.) The potential in the equatorial plane (θ = π/2) is zero.