 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe rate constant for the first-order decomposition of H2O2 is given by the following equation: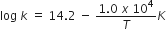
Calculate Ea for this reaction and rate constant k if its half-life period be 200 minutes. (Given: R = 8.314 JK–1mol–1).
For a reaction: 
rate =k
i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
ii) Write the unit of k.
For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
C2H5Cl (g) --> C2H4 (g) +HCl(g)
T/s Total pressure/atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2=0.301, log =0.4771, log 4 =0.6021)
The thermal decomposition of HCO2H is a first-order reaction with a rate constant of 2.4 x 10-3 s-1 at a certain temperature. Calculate how long will it take for three-fourths of the initial quantity of HCO2H to decompose.
(log 0.25 = - 0.6021)
What do you understand by the rate law and rate constant of a reaction?
Identify the order of a reaction if the units of its rate constant are:
(i) L-1 mol s-1
(ii) L mol-1 s-1The rate law can be defined as an expression containing the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants and products. It is an expression in which the rate of reaction is given in terms of the molar concentration of the reactants, with each term raised to some power, which may or may not is the stoichiometric coefficient of the reacting species in a balanced chemical equation. The rate constant can be defined as the rate of the reaction when the concentration of each of the reactant is taken as unity.
Example: 2NO(g) + O(g)---> 2NO2(g)
The rate expression for the above reaction can be written as follows:
Rate = k [NO]2 [O2] (Experimentally determined)
Now, if the concentration of NO and O2 is taken to be unity, then the rate constant is found to be equal to the rate of the reaction.
(i) Comparing power of mole in L-1 mol s-1 and (mol L-1)1-n s-1,
We get
1 = l – n => n = 0 i.e., zero order reaction
(ii) Again comparing power of mole in L mol-1 s-1 and (mol L-1)1-n s-1
We get
–1 = 1 – n => n = 2, i.e., second order reaction.For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as,
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve?
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at a constant volume :
SO2Cl2 (g) → SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
|
Experiment |
Time/s−1 |
Total pressure/atm |
|
1 |
0 |
0·4 |
|
2 |
100 |
0·7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given : log 4 = 0·6021, log 2 = 0·3010)
For a reaction R → P, half-life (t1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction?
